News
Inside the ‘New Cold War’: How Countries Are Competing for Space and Resources Beyond Earth

Right now, there’s a new space race underway, but it’s not about just getting to the Moon or planting flags. This time, it’s all about finding and using resources out there that could change the game both in space and back on Earth.
Countries like the U.S. and China are leading this charge, each working on big plans for tapping into things like lunar water ice and valuable minerals. And it’s not just governments involved. Private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin, along with newer startups, are jumping in too, pushing technology to make space mining a reality.
In this article, we’ll look at who’s involved, what they’re planning, and why it matters. With so many players aiming to unlock the potential of space, this race is setting the stage for what could be a whole new era of exploration and opportunity.
The Promise of Space Resources: Why Lunar and Extraterrestrial Resources Matter

Why is there so much interest in mining space? The answer lies in resources that could transform both space missions and life back on Earth. Take the Moon, for example. It’s not just a dry, dusty rock; its poles contain water ice, a resource with incredible potential. In space, water isn’t just for drinking—it can be split into hydrogen and oxygen, meaning it could provide breathable air for astronauts and even fuel for rockets. This makes it much more than a convenience; it’s a game-changer for anyone aiming to explore deeper into the solar system.
Besides water, the Moon and other nearby bodies contain valuable minerals and elements that are tough to find on Earth. One standout is helium-3, a rare isotope that has big potential as a clean energy source. On Earth, helium-3 could be used for nuclear fusion, a process that promises almost unlimited energy with hardly any pollution. It’s an exciting idea, especially as the world looks for cleaner, more sustainable power options.
For governments and private companies, tapping into these resources isn’t just about exploration—it’s about having a shot at future economic power and energy security. Whoever can reach, mine, and use these resources first could lead the next era of technology and even shift global power dynamics. Imagine a future where space minerals fuel new industries, where lunar water supports missions to Mars, and where helium-3 powers entire cities back on Earth. That’s the kind of future these nations and companies have in mind, and it’s why so many are investing heavily in technology to make space mining a reality.
In short, space resources could open the door to long-term missions, a self-sustaining space economy, and solutions to some of Earth’s biggest challenges. It’s not just science fiction anymore—it’s the next big step.
Futuristic Projects: Governments and Private Companies Leading the Charge
Making space mining a reality isn’t easy. It takes cutting-edge tech, major investments, and some seriously ambitious projects. Governments and private companies are both throwing their hats in the ring, each working on plans that could bring space resources within reach.
NASA’s Artemis program is probably the best-known effort right now. Their big goal? To set up a long-term human presence on the Moon. Artemis includes plans to build something called the Lunar Gateway, which is basically a small space station that’ll orbit the Moon and serve as a jumping-off point for astronauts. With the Gateway in place, NASA and its partners can start to dig deeper into the Moon’s surface and figure out how to live and work there. What’s interesting is that this isn’t just a U.S. project—more than 40 countries have signed on through the Artemis Accords, committing to work together as they explore the Moon.
China has its own ambitious plan through the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS). While it’s not as widely advertised, China’s goals are just as big. Teaming up with Russia, they’re working on a state-led lunar base they hope to establish by the late 2020s. China’s approach is a bit different from NASA’s. While NASA partners with private companies, China’s government is running the show, keeping close control over their technology and resources. They’re very focused on making this a strategic win, both in terms of tech and economic advantage.
Private Companies: Pushing Space Tech to New Heights
Private companies are also jumping into the race to make space resources accessible. SpaceX, with its reusable rockets, has already cut down the cost of going to space, and they’re working on lunar landers to support NASA’s missions. Then there’s Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos’s space venture, which is developing its own lunar landers and exploring ways to create a sustainable human presence on the Moon.
On top of that, a wave of startups is getting in on the action. Some are building mining robots that could dig into the Moon’s surface on their own, while others are focused on habitats that could help people live there longer. A big trend is something called “in-situ resource utilization,” or ISRU. This basically means using what’s already on the Moon—like water ice or minerals—so future missions don’t have to bring everything from Earth. It’s all about figuring out how to live off the land in space.
Together, these government programs and private projects are laying the foundation for what could become a true space economy. Governments are building the infrastructure, while private companies are coming up with ways to make mining and resource use practical and affordable. With each new mission, the idea of using space resources to fuel future exploration—and maybe even sustain life beyond Earth—starts to feel a bit more real.
Different Strategies for Space Exploration and Resource Access
The U.S. and China are both serious about leading the way in space, but they’re going about it in pretty different ways. Each country has its own strategy and is picking allies that line up with its goals, creating two very different approaches to the future of space.
The U.S. Game Plan: Teamwork and Partnerships
The U.S. is big on working with others. Through NASA’s Artemis program, they’re teaming up with other countries and private companies to share resources and knowledge. The idea here is that, by joining forces, everyone can make faster progress. The Artemis Accords—signed by over 40 countries—lay out some basic rules for cooperation, like keeping things transparent, peaceful, and fair when it comes to using resources. It’s a way to make sure everyone is on the same page from the start, especially as interest in space mining grows.
NASA also relies a lot on private companies, like SpaceX and Blue Origin, to help bring new technology into the mix. These companies are leading the charge in innovation, and by working with them, NASA doesn’t have to take on all the risk or cost alone. This approach lets the U.S. stay flexible and pull from a wide network of players, from governments to private businesses, all working toward a shared vision for space.

China’s Strategy: A More Solo Approach
China, on the other hand, is keeping things closer to home. Their government runs the show, leading its space missions through the China National Space Administration (CNSA). China has teamed up with Russia to create a lunar research station, but it’s mostly a state-controlled project. This means China is sticking to its own plans, controlling the technology and resources without relying much on other countries or companies. By keeping their space projects in-house, they can focus on their own long-term goals without needing outside support.
China’s centralized approach has some perks—it allows for quicker decisions and makes it easier to stay focused on specific goals. But it also means they aren’t building as many international partnerships, which could become an issue if space exploration gets even more collaborative down the line.
Two Different Paths to the Future of Space
These two strategies reflect two different visions for space. The U.S. is betting on teamwork and open partnerships, while China is focusing on self-reliance and strategic control. Both approaches have their upsides and challenges, and the way they unfold could have a big impact on who gets access to valuable space resources in the years to come.
In the end, this mix of competition and cooperation is likely to shape the rules of space exploration as we know it, with countries and companies figuring out how to work (and sometimes compete) side by side in a brand-new frontier.
The High Stakes and Big Dreams of the New Space Race

We’re in the middle of something exciting—a space race that’s all about using what’s out there to build something new. This isn’t just about putting flags on distant planets anymore. It’s about tapping into resources like water ice, rare minerals, and helium-3 on the Moon—things that could totally change how we live and work, both here on Earth and out there in space.
Sure, there’s competition. But getting this right will take some teamwork too. With so many countries and companies involved, figuring out how to share, cooperate, and play fair is going to be key. If we can strike that balance, space could become a resource that works for everyone.
This race is really about what’s possible. It’s about turning big ideas into real solutions and seeing if space can become a part of our world in ways we’ve only dreamed about. The journey’s just beginning, and where it leads could be incredible.
News
Musk Breaks World Record, Losing The Most Personal Wealth Of Anybody In History

Elon Musk, a name often associated with groundbreaking innovation and staggering success, has now made history for a completely unexpected reason—one that no billionaire would ever aspire to. Despite holding titles like “visionary entrepreneur” and “world’s richest person,” Musk’s financial journey recently took a dramatic turn that has left many stunned. A record-breaking loss, fueled by shifting markets and high-stakes decisions, has placed him in the Guinness World Records—but not for reasons you’d expect.
What led to this extraordinary loss? How did one of the most powerful figures in technology see his fortune shrink at such an unimaginable scale?
The Numbers Behind the Record
Elon Musk’s financial journey has been a rollercoaster of unprecedented highs and staggering lows. In November 2021, his net worth peaked at approximately $320 billion, making him the world’s richest person at the time. However, by January 2023, his fortune had plummeted to around $138 billion, marking a loss of about $182 billion. Some estimates suggest the losses could be as high as $200 billion.
This dramatic decline earned Musk a Guinness World Record for the largest loss of personal fortune in history, surpassing the previous record held by Japanese tech investor Masayoshi Son, who lost $58.6 billion in 2000.
The primary driver behind Musk’s financial downturn was the significant drop in Tesla’s stock price, which fell by 65% in 2022. This decline was influenced by various factors, including missed delivery targets, supply chain issues, and increased competition in the electric vehicle market. Despite these setbacks, Musk’s wealth remains substantial. As of December 2024, his net worth is estimated at $455 billion, primarily due to his ownership stakes in Tesla and SpaceX.
This resurgence underscores the volatile nature of wealth tied to stock performance and the rapid fluctuations that can occur in the tech industry.
Why Did Musk’s Wealth Plummet?

Elon Musk’s unprecedented loss of personal wealth can be attributed to several key factors:
1. Decline in Tesla’s Stock Value
Tesla’s stock experienced a significant decline, dropping by 65% in 2022. This downturn was influenced by various factors, including missed delivery targets, supply chain issues, and increased competition in the electric vehicle market.
2. Acquisition of Twitter
Musk’s acquisition of Twitter for $44 billion in October 2022 had a substantial impact on his net worth. To finance the deal, he sold a considerable number of Tesla shares, which contributed to the decline in Tesla’s stock price. Additionally, the acquisition led to concerns among investors about Musk’s focus and the potential impact on Tesla’s operations.
3. Market Volatility and Economic Factors
The broader market volatility and economic factors also played a role in the decline of Musk’s wealth. Fluctuations in the stock market, changes in investor sentiment, and economic uncertainties contributed to the decrease in the value of Musk’s holdings.
The Ripple Effects
Elon Musk’s significant financial losses have had far-reaching implications, affecting not only his personal wealth but also Tesla’s shareholders, the company’s market perception, and the broader electric vehicle (EV) industry.
The decline in Tesla’s stock price has directly impacted its investors. Notably, the top ten Tesla shareholders have collectively lost approximately $132.5 billion due to the company’s stock downturn. Musk himself, as the largest shareholder with a 14.1% stake, has personally lost $47.9 billion from the decline.
Musk’s acquisition of Twitter and the subsequent diversion of his attention have raised concerns among Tesla investors. Some shareholders fear that his focus on other ventures could negatively impact Tesla’s operations and strategic direction. This apprehension has contributed to increased market volatility and a decline in investor confidence.
Musk’s compensation package has been a subject of legal scrutiny. A Delaware judge recently voided his $56 billion pay package, citing concerns over its fairness and the approval process. This decision has prompted discussions about corporate governance practices at Tesla and the influence of Musk’s leadership on the company’s decision-making processes.
Tesla’s market performance serves as a bellwether for the broader EV industry. The company’s stock decline has led to increased scrutiny of the EV market’s stability and growth prospects. Investors and industry analysts are closely monitoring how Tesla navigates these challenges, as its strategies and performance are often seen as indicators of the industry’s overall health.
Musk’s Response to the Crisis

Elon Musk has navigated the financial turbulence with a blend of public optimism and strategic focus. In December 2022, amidst Tesla’s stock decline, he addressed employees, urging them not to be “bothered by stock market craziness” and emphasizing the company’s strong performance.
Musk’s confidence in Tesla’s future is evident. He has stated that the company’s “long-term fundamentals are extremely strong,” suggesting that short-term market fluctuations do not deter his vision.
In response to concerns about his focus following the Twitter acquisition, Musk has reiterated his commitment to Tesla. He continues to lead the company towards ambitious goals, including the development of new vehicle models and advancements in autonomous driving technology.
Despite the financial setbacks, Musk’s proactive communication and unwavering confidence aim to reassure investors and stakeholders of Tesla’s resilience and his dedication to the company’s mission.
Where Musk Stands Now
Elon Musk’s financial trajectory has been marked by significant fluctuations, yet as of December 2024, he has reached unprecedented heights in personal wealth. According to Bloomberg, Musk’s net worth has surpassed $447 billion, making him the first individual to exceed the $400 billion threshold.
This remarkable rebound is largely attributed to the impressive performance of his ventures, particularly Tesla and SpaceX. Tesla’s stock has experienced a substantial surge, with shares closing at an all-time high of $424.77, reflecting a 71% increase this year. Similarly, SpaceX’s valuation has soared, contributing significantly to Musk’s wealth accumulation.
In contrast, Bernard Arnault, CEO of LVMH, has seen his net worth decline to approximately $160.3 billion, positioning him among the top five richest individuals globally.
The Billionaire’s Unprecedented Journey: A Story of Rise, Fall, and Resilience
Elon Musk’s record-breaking loss of wealth, while staggering, is a reflection of the volatile nature of markets, personal investments, and billion-dollar ventures. Musk’s story is not simply one of financial decline but also of adaptation and resilience. Despite the massive wipeout, his ventures—Tesla, SpaceX, and even Twitter—continue to shape industries and break barriers.
While Musk’s losses are unprecedented in scale, they serve as a reminder of the risks tied to success in high-stakes industries. Markets may dip, critics may emerge, but Musk’s unwavering optimism and entrepreneurial drive remain constant. As the future unfolds, the world will continue watching how this modern-day innovator navigates triumphs and setbacks, always pushing toward the next big milestone.
Ancient History
Human Civilization At Junction Between An Evolutionary Leap Or An Authoritarian Collapse

Imagine standing at the edge of a vast fork in the road, one path glimmering with the promise of innovation and unity, the other shadowed by oppression and decay. Throughout history, civilizations have faced moments of reckoning—turning points where the choices of a generation ripple through centuries. But today, with accelerating technological advancements and looming global challenges, humanity is hurtling toward a crossroads unlike any other.
Will we unlock a future defined by collaboration, unprecedented breakthroughs, and sustainability? Or will we succumb to the forces of division, authoritarian control, and ecological collapse? With each passing day, the decisions we make—individually and collectively—draw us closer to one of these realities.

The Evolutionary Leap: Embracing Innovation and Unity
Humanity has always been driven by a remarkable capacity for progress. From harnessing fire to exploring the cosmos, our collective ability to innovate and adapt has shaped the course of history. Today, we stand on the cusp of what could be our greatest leap yet—one marked by technological breakthroughs, cultural unity, and sustainable solutions to the challenges we face.
Technological Breakthroughs as Catalysts
Advancements in artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and biotechnology offer unprecedented opportunities to redefine how we live. For instance, renewable energy innovations like solar-powered microgrids could provide sustainable power to even the remotest regions, bridging gaps between developed and developing nations. Similarly, AI holds the potential to revolutionize industries, from personalized medicine to climate modeling, fostering global solutions to systemic problems.
However, these advancements are not just about convenience—they carry the promise of uniting us. Imagine a world where diseases are eradicated through collective research or where climate crises are mitigated by shared technological resources. These possibilities illustrate how progress, when guided by ethics and equity, can be a force for collective upliftment.
The Role of Global Interconnectedness
In an era defined by globalization, the barriers that once divided nations and cultures are breaking down. The internet, social media, and global trade have created an interconnected world where ideas, cultures, and technologies can flow freely. This interdependence is not merely a byproduct of progress; it is a tool for collaboration. From international climate agreements to cross-border scientific partnerships, humanity’s ability to work together is proving critical in addressing global issues.
Experts suggest that the challenges we face today—climate change, pandemics, and economic inequality—are too complex for any one nation to tackle alone. As historian Yuval Noah Harari puts it, “The only solution to global problems is global cooperation.” This underscores the need for unity as we strive for a future that benefits all.

Cultural Evolution: Moving Toward Unity
Technological and environmental progress alone isn’t enough to propel humanity forward; cultural evolution is equally vital. The rise of grassroots movements advocating for equality, sustainability, and justice signals a shift in collective consciousness. Younger generations, in particular, are leading calls for systemic change, demanding accountability from governments and corporations alike.
This cultural shift is crucial for creating a shared vision of humanity’s future. As societies begin to prioritize empathy, collaboration, and long-term thinking, the possibility of an evolutionary leap becomes not just a dream but a tangible path forward.
From cutting-edge technology to a growing sense of global unity, the potential for evolution is real—but it requires intentional choices. For every opportunity to move forward, there’s an equal risk of falling back into old patterns of division and control. This leads us to the darker road humanity might take: one of authoritarian collapse.
The Authoritarian Collapse: A Descent into Dystopia
As humanity stands at a crossroads, the dark specter of authoritarianism looms large. History has shown that crises—be they economic, political, or environmental—often provide fertile ground for the consolidation of power. Under the guise of ensuring security and stability, leaders and governments have historically curtailed freedoms, tightened control, and eroded democratic norms. Today, the same trends are emerging, with global crises increasingly being used as pretexts for authoritarian rule.
Surveillance technology, originally intended to protect, has become a double-edged sword. In many parts of the world, facial recognition, data analytics, and AI-driven monitoring systems are being leveraged to suppress dissent and manipulate public opinion. The loss of privacy under such regimes not only undermines individual freedoms but also deepens societal divisions, as people are reduced to mere data points in systems they cannot influence. The result is a chilling landscape where citizens are subjected to pervasive control, creating an illusion of safety while freedom disappears.
Even democracies are not immune. The erosion of institutional checks and balances, coupled with rising polarization and misinformation, has led to a global trend of “democratic backsliding.” This slow decay of democratic norms creates openings for authoritarian tendencies to grow. If these patterns continue unchecked, the promise of progress risks being overshadowed by regression, leaving humanity vulnerable to a future defined not by collaboration and innovation, but by control and division.
The Role of Technology: Savior or Saboteur?
Technology stands at the center of humanity’s crossroads, offering both immense potential and significant peril. On one hand, it has fueled extraordinary advances—artificial intelligence capable of predicting pandemics, renewable energy solutions combating climate change, and communication tools connecting billions of people worldwide. These innovations hold the power to drive an era of unparalleled collaboration and progress, pushing humanity toward a brighter future.
However, the same technologies that promise evolution can also serve as instruments of control. AI, for example, has been weaponized for mass surveillance and social manipulation, with authoritarian regimes using it to monitor citizens and suppress dissent. Social media, designed to foster connection, often amplifies misinformation and fuels societal polarization. The misuse of these tools raises ethical dilemmas, as unchecked technological power increasingly threatens privacy, autonomy, and freedom.
The outcome depends on how humanity wields these tools. Will we establish ethical guidelines and global cooperation to ensure technology serves as a force for good? Or will we allow it to deepen existing divides and solidify authoritarian control? The answer lies not in the technology itself, but in the choices we make about its development and governance—a reflection of our collective values and priorities.
Environmental Urgency: A Ticking Clock
The planet’s rapidly deteriorating health adds urgency to humanity’s crossroads, intertwining environmental crises with societal and political challenges. Climate change, biodiversity loss, and resource depletion are no longer distant threats; they are immediate realities that exacerbate inequalities, spark conflict, and destabilize nations. These environmental pressures could either catalyze global cooperation or drive authoritarian responses under the guise of emergency measures.
Extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and food insecurity have already begun to displace millions, creating waves of climate refugees and straining international systems. In many cases, governments respond with isolationist policies, fortifying borders and centralizing power rather than addressing root causes. This reactionary approach not only deepens global divisions but also paves the way for authoritarian governance under the pretext of maintaining order during ecological crises.
Yet, the same environmental challenges also hold the potential to unite humanity. Efforts like the Paris Agreement demonstrate that large-scale collaboration is possible when the stakes are high. By embracing renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and conservation efforts, nations can work together to combat ecological degradation and build resilience. The question remains whether humanity will rise to the challenge or succumb to fear and division, allowing environmental collapse to accelerate societal decline.
What’s Next? Key Decisions for Humanity’s Future
The path forward demands intentional choices that will define humanity’s trajectory for generations to come. At this critical juncture, governments, organizations, and individuals must confront pressing questions: Will we prioritize collaboration over conflict, equity over division, and sustainability over short-term gain? The answers to these questions will determine whether we evolve toward progress or collapse under pressure.
Leadership rooted in adaptability and ethical responsibility is essential. Policymakers must prioritize frameworks that balance technological innovation with strict ethical oversight, ensuring advancements benefit humanity as a whole rather than deepening inequalities. Similarly, grassroots movements advocating for environmental justice, human rights, and democratic accountability play a vital role in shaping the global agenda and holding power structures accountable.
Perhaps most importantly, individuals have a stake in shaping the future. Everyday choices—consuming sustainably, advocating for transparency, and participating in civic action—contribute to the larger narrative of humanity’s direction. As the world faces challenges of unprecedented scale, the collective power of billions of small actions could tip the balance. Whether humanity takes the path of evolution or collapse depends on our willingness to embrace cooperation and confront these existential challenges with courage and purpose.
Humanity’s Great Gamble
Humanity stands at a pivotal moment, poised between two vastly different futures. The choices we make today will determine whether we unlock a new era of innovation, unity, and sustainability, or spiral into authoritarianism and societal fragmentation. The stakes are extraordinary—this is not merely about survival but about defining the essence of what it means to be human in the face of adversity.
The potential for an evolutionary leap is within reach, driven by technology, collective action, and the shared challenges that bind us together. But this progress hinges on our ability to act with intention, ensuring that power is distributed equitably, freedoms are protected, and the planet’s well-being remains central to our decisions. Equally, we must resist the pull of fear and division that could steer us toward authoritarian collapse.
The path forward is neither predetermined nor easy, but it is ours to choose. As individuals, communities, and nations, we hold the tools to shape the future—a future that will either be defined by progress and possibility or by regression and control. The question remains: will we rise to the occasion, or will we let the moment slip through our fingers? The time to decide is now.
News
South Park Creators Use ChatGPT To Co-Write Episode About AI

In a world where algorithms compose music, paint masterpieces, and even mimic human conversations, the line between human creativity and artificial intelligence grows blurrier by the day. But what happens when AI steps into one of television’s most irreverent, boundary-pushing realms? Enter South Park, a show that has long thrived on poking fun at the absurdities of modern life.
In a bold move, creators Trey Parker and Matt Stone turned to ChatGPT—yes, the same AI tool you might use to draft emails or brainstorm ideas—to co-write an episode. It’s a collaboration that raises a tantalizing question: can a machine ever match the razor-sharp wit and satire of one of the world’s most iconic shows? And, perhaps more importantly, what does this experiment say about the future of storytelling in a tech-driven age?

Why ChatGPT? The Perfect Tool for Satire
For a show like South Park, which has spent decades lampooning the absurdities of modern life, the decision to use ChatGPT as a co-writer was anything but arbitrary. Artificial intelligence, particularly tools like ChatGPT, has surged into the spotlight as one of the most transformative and divisive technologies of our era. These tools are no longer confined to niche applications; they are now used to write essays, compose music, and even assist with creative brainstorming. The rise of AI has sparked heated debates about the nature of creativity, originality, and what it truly means to be human in an increasingly automated world.
Trey Parker and Matt Stone, the masterminds behind South Park, recognized the satirical potential of this cultural moment. ChatGPT isn’t just an advanced algorithm; it’s a symbol of a society struggling to keep pace with rapid technological change. By inviting AI into their own creative process, they tapped into a broader cultural phenomenon, where people both marvel at AI’s capabilities and question its implications. This choice allowed the creators to address head-on the uneasy coexistence of human creativity and machine efficiency—while still delivering the irreverent humor the show is famous for.
Beyond its practical utility, the decision to collaborate with ChatGPT underscores South Park’s unique ability to adapt to the times. Just as the show has previously tackled the rise of social media, cancel culture, and political correctness, this episode serves as a critique not just of AI’s growing role in society, but also of our collective obsession with it. By using ChatGPT to co-write their episode, Parker and Stone blurred the line between satire and reality, crafting a story that holds up a mirror to our fears, fascinations, and the inevitable questions of authenticity in a tech-dominated future. It’s a move that cements South Park’s status as a cultural touchstone for navigating modern life’s most pressing—and often most ridiculous—trends.
Inside the Episode: A Satirical Take on AI
The episode in question dives headfirst into the world of artificial intelligence, blending South Park’s signature humor with a sharp critique of how AI tools like ChatGPT are reshaping our interactions and decision-making. The episode was “written by Trey Parker and ChatGPT,” showcasing a unique partnership that brought AI into the heart of its satirical storytelling. In true South Park fashion, the storyline doesn’t shy away from pushing boundaries, using comedy as a lens to examine the absurdity and ethical dilemmas surrounding the increasing reliance on AI in everyday life.
At the heart of the episode lies a storyline involving Stan Marsh, who cleverly uses ChatGPT to compose text messages that help him navigate relationships. What starts as a seemingly harmless hack soon spirals into a hilarious exploration of AI’s unintended consequences. The plot unfolds in a way that is both comically exaggerated and surprisingly reflective of real-world concerns. How much of our communication is authentic when we outsource it to machines? Can AI help us build better connections, or does it merely serve as a shortcut that undermines genuine human interaction? These are the kinds of questions the episode subtly raises, all while delivering punchlines that keep viewers laughing.

Behind the Scenes: How AI Shaped the Script
Behind the humor and sharp satire of the South Park episode lies a fascinating creative experiment: the integration of ChatGPT into the writing process. The creators, Trey Parker and Matt Stone, didn’t just use ChatGPT in isolation—they leaned on resources from their AI-focused studio, Deep Voodoo, which recently received $20 million in funding to develop “deep fake technology, cost-effective visual effects services, and original synthetic media projects.” This collaboration highlights the creators’ commitment to exploring the cutting edge of technology to enhance their storytelling.
ChatGPT’s role wasn’t just a gimmick; it was a deliberate choice to test the limits of AI as a creative partner. The tool was used to help generate dialogue and plot ideas, blending the AI’s output with the creators’ signature wit and storytelling style. The result was a script that felt distinctly South Park—irreverent, insightful, and brimming with absurdity—while also showcasing the unique quirks and limitations of AI-generated content. Parker and Stone reportedly found humor in the way ChatGPT would occasionally misinterpret tone or produce overly polished text, which they then adapted to fit the show’s chaotic and edgy voice.
What made the process particularly interesting was the balance between human oversight and AI contribution. Parker and Stone treated ChatGPT as an idea generator rather than an independent writer. While the AI could produce a flood of suggestions, it lacked the cultural awareness and comedic nuance that define South Park’s tone. The creators had to sift through its outputs, tweaking and shaping them to fit the show’s vision, ensuring the final product retained its sharp, satirical edge. This meticulous approach showcased how AI can augment creativity, but also emphasized the irreplaceable role of human insight in creating truly impactful content.
This collaboration also offered a glimpse into how AI might shape the future of storytelling. While ChatGPT was instrumental in generating ideas, the creators found themselves reflecting on its limitations—particularly its inability to grasp subtext or infuse content with emotional depth. The experiment demonstrated that while AI can accelerate certain aspects of the creative process, it works best as a tool in the hands of skilled creators. For Parker and Stone, this blending of AI’s efficiency and human intuition was key to making the episode both innovative and authentically South Park.
Redefining Creativity: Will AI Rewrite the Rules of Storytelling?
The collaboration between South Park’s creators and ChatGPT has sparked broader discussions about the future of creativity in a world increasingly influenced by artificial intelligence. Could this be the beginning of a new era in storytelling where machines play a significant role, or is it merely a passing trend, showcasing AI’s novelty rather than its depth? These questions are at the heart of the debate about AI’s place in creative industries.
One of the most compelling aspects of this experiment is the way it challenges the traditional concept of authorship. For centuries, storytelling has been considered an innately human endeavor, fueled by emotion, experience, and cultural nuance. AI, while undeniably efficient, operates differently—it processes vast amounts of data to generate content based on patterns rather than personal insight or inspiration. This raises the question: can AI truly create, or does it simply imitate? In the case of South Park, the balance between human ingenuity and machine output became critical. While ChatGPT contributed to the episode’s dialogue and ideas, Parker and Stone’s creative instincts ultimately shaped the material into something meaningful and entertaining.
The implications of AI-driven storytelling extend far beyond the realm of television. In industries ranging from advertising to filmmaking, AI is already being used to generate scripts, conceptualize campaigns, and even edit content. Proponents argue that these tools can streamline workflows, spark innovative ideas, and democratize creativity by making advanced resources accessible to more people. Critics, however, warn of the potential risks: the homogenization of content, the loss of authentic human voices, and the ethical concerns surrounding AI’s impact on employment in creative fields.
AI Meets Creativity: A Bold Step, Not a Replacement
South Park’s experiment with ChatGPT represents a pivotal moment in the intersection of technology and creativity. By blending AI-generated content with human wit and storytelling expertise, Trey Parker and Matt Stone didn’t just create a memorable episode—they sparked a larger conversation about what it means to be creative in a tech-driven world. The episode serves as a reflection of our fascination with AI, offering both humor and insight into its potential and limitations.
At its core, this experiment underscores a simple truth: while AI can enhance the creative process, it cannot replace the human touch. The ability to infuse stories with emotion, cultural context, and originality remains uniquely human, even as machines grow more sophisticated. What South Park achieved wasn’t just another episode—it was a bold step into the future of storytelling, one that challenges us to think critically about the role of technology in shaping the narratives of our lives.
As the lines between human and machine creativity continue to blur, one thing is clear: the art of storytelling is evolving, and experiments like this are just the beginning. Whether AI becomes a revolutionary tool or a passing curiosity will depend on how creators choose to engage with it. For now, South Park has shown that even in a world of algorithms, satire and humor are still best delivered with a distinctly human touch.
Awareness
Genetically Modified Mosquitoes Have Been Released in the US

Imagine a future where humans can rewrite the very fabric of life, tinkering with nature to solve some of the world’s deadliest problems. That future isn’t decades away—it’s already here. In the US, thousands of genetically modified mosquitoes have been unleashed into the wild, their mission to combat diseases like dengue, Zika, and malaria. These tiny, gene-edited creatures are designed to self-destruct after disrupting mosquito populations, a biological trick that could reshape ecosystems and public health strategies alike.
But are we solving one problem only to create another? While advocates champion this as a breakthrough in disease control, critics warn of unintended consequences: ecological ripple effects, ethical quandaries, and the unsettling precedent of genetic experimentation in the wild. Are genetically modified mosquitoes a modern miracle—or Pandora’s box?

How Do Genetically Modified Mosquitoes Work?
At first glance, these modified mosquitoes appear no different from their natural counterparts. However, beneath their delicate wings lies a scientific breakthrough that turns nature against itself. Created by the biotech firm Oxitec, these mosquitoes have been engineered with a self-limiting gene designed to curb the population of Aedes aegypti—a species notorious for spreading diseases like dengue, Zika, and yellow fever.
Here’s how it works: male mosquitoes, which don’t bite or spread disease, are altered to carry a gene that ensures their offspring won’t survive to adulthood. When these genetically modified males are released into the wild, they mate with female mosquitoes. The resulting larvae inherit the lethal gene and die before they can reproduce, gradually reducing the overall mosquito population. In theory, this approach targets the root of mosquito-borne illnesses without the need for harmful pesticides.
The technology has been tested in Brazil, Panama, and other parts of the world with some success, leading to its experimental deployment in the US. Supporters hail it as a precise and environmentally friendly solution to a deadly problem. Yet, as with any biological intervention, the devil is in the details. What happens if this delicate system goes awry? And are these engineered insects as controllable as scientists claim? The answers remain as elusive as the mosquitoes themselves.
Where and Why: The Scope of the Release
The release of genetically modified mosquitoes in the United States marks a new chapter in the battle against mosquito-borne diseases. Florida and Texas, regions notorious for their warm climates and mosquito-friendly environments, have been selected as testing grounds for Oxitec’s genetically altered insects. These areas experience seasonal outbreaks of diseases like dengue and Zika, making them prime candidates for this experimental solution.
Oxitec’s program, approved by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), involves the release of millions of genetically modified male mosquitoes into these communities. The initiative is framed as an effort to curb the population of Aedes aegypti, a mosquito species responsible for transmitting these illnesses. By targeting this specific species, proponents argue, the approach minimizes harm to other wildlife while focusing on a major public health threat.
However, the scale and location of the release have sparked heated debate. Some residents and environmental advocates question whether adequate precautions have been taken. Could these experiments impact local ecosystems, or lead to unintended consequences for humans and wildlife? These concerns have amplified the scrutiny surrounding the program, raising questions about the balance between scientific ambition and ecological stewardship.

Concerns and Controversies: Ethical and Ecological Implications
Critics have voiced concerns about the potential ecological consequences of reducing or altering Aedes aegypti populations. While these mosquitoes are a public health threat, they are also part of the food chain, serving as prey for various species like birds, bats, and other insects. Disrupting their population could inadvertently affect predator species and ripple through ecosystems in ways that scientists cannot fully predict.
The challenge lies in the inherent complexity of ecosystems, which cannot be replicated in a controlled laboratory environment. “Nature is full of interdependencies,” argue ecologists, highlighting the potential for cascading effects that might arise from tampering with a single species.
The Risk of Genetic Spillover
A key concern surrounding genetically modified mosquitoes is the risk of unintended genetic interactions. If these engineered mosquitoes breed with other species, could their genetic modifications spread? While Oxitec assures the public that the self-limiting gene is designed to prevent survival in offspring, skeptics caution that nature has a way of defying human expectations.
This uncertainty raises fears about mutations or genetic spillover, which could result in unforeseen consequences. What starts as a targeted intervention could potentially lead to new challenges, creating a problem as significant as the one it aims to solve.
Ethics and Public Consent
Beyond the ecological risks, the ethical implications of these trials have sparked widespread debate. Many residents in areas like Florida and Texas have voiced their frustration over the lack of transparency and limited community input before these experimental releases began. For some, this feels like a decision imposed upon them, with insufficient regard for their consent or concerns.
Additionally, activists point out the broader ethical question: should humans have the right to manipulate nature so fundamentally? While proponents argue the approach is necessary to combat deadly diseases, critics urge caution, warning that the long-term consequences of such interventions remain unknown.
The debate surrounding genetically modified mosquitoes extends beyond science—it delves into our responsibilities as stewards of the natural world and forces us to confront the ethical boundaries of innovation.
Health Risks and Unintended Consequences
A significant concern raised by skeptics is the possibility of resistance developing within mosquito populations. If some mosquitoes manage to survive the effects of the self-limiting gene, natural selection could favor those individuals, potentially leading to a stronger, more resistant population. This raises questions about the long-term sustainability of this approach and whether it could inadvertently create a more challenging problem than the one it aims to solve.
Additionally, while Oxitec assures that the genetic modifications are designed to be specific and controlled, concerns linger about the unpredictability of nature. Critics worry that unexpected mutations could arise from the interaction of genetically modified mosquitoes with their environment, leading to consequences that have not been fully anticipated.
Impact on Human and Environmental Health
Although the modified male mosquitoes are non-biting and their gene alterations are intended to be contained within the Aedes aegypti species, doubts remain about their broader impact. Some fear the potential for unintended interactions with other species or the environment. These concerns, while largely theoretical, underscore the need for extensive, long-term studies to ensure the safety of such interventions.
Andrea Leal, the head of mosquito control in the Florida Keys, acknowledges both the promise and the uncertainty of these emerging technologies, stating, “The good news is we’ve got these emerging technologies that show great promise in reducing Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.” While this optimism is shared by some, others argue that the risks are too significant to ignore without more comprehensive research.
Ecosystem Imbalances
Another critical issue is the potential ecological imbalance that could result from targeting Aedes aegypti. As a species integral to certain ecosystems, their reduction or elimination could disrupt food chains, impacting predators like birds and bats that rely on mosquitoes as a food source. Additionally, reducing the population of Aedes aegypti might open ecological niches for other, possibly more harmful, mosquito species to thrive. This risk highlights the complexities of meddling with natural systems, even with the best intentions.
As these concerns accumulate, it becomes clear that the introduction of genetically modified mosquitoes is as much a test of ecological stewardship as it is a scientific innovation. Balancing potential benefits with these risks remains a daunting challenge for researchers and policymakers alike.
The Bigger Picture: Is This the Right Approach?
The release of genetically modified mosquitoes is touted as a breakthrough, but many view it as a reckless gamble with nature. Traditional methods like eliminating stagnant water and using biological controls such as Wolbachia bacteria have proven effective without the risks of genetic modification. Critics argue these safer alternatives are being overshadowed by corporate interests pushing untested and controversial technologies, risking ecological disruptions and public trust.
Despite claims of success, the long-term safety and effectiveness of genetically modified mosquitoes remain unverified. Andrea Leal, head of mosquito control in the Florida Keys, said, “The good news is we’ve got these emerging technologies that show great promise in reducing Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.” However, “promise” does not equate to evidence, and rushing to release these insects without full understanding risks unintended consequences that could worsen the problem.
Ethically, this project has sparked outrage over a lack of transparency and public consent. Many residents feel like unwilling participants in an experiment that could have unknown repercussions for their environment and health. Critics warn that meddling with nature at this scale risks creating new ecological imbalances while eroding public confidence in scientific oversight, making these trials more of a warning than a solution.
A Warning for the Future
The release of genetically modified mosquitoes is a stark reminder of the complexities and ethical dilemmas inherent in tampering with nature. While the intention to combat deadly diseases like dengue and malaria is noble, the risks and uncertainties surrounding this approach cannot be ignored. From potential ecological disruptions to unanswered questions about long-term safety, this experiment serves as a cautionary tale about the consequences of prioritizing rapid deployment over thorough research and public consent.
Critics argue that the rush to embrace genetic engineering reflects a dangerous overconfidence in humanity’s ability to control nature. Without clear evidence of success or a transparent process involving affected communities, these projects risk alienating the public and jeopardizing ecosystems in ways that may be irreversible. The promise of genetically modified organisms must be balanced against the real-world consequences they could unleash.
As the debate continues, it is essential to prioritize caution, transparency, and public involvement. Scientific innovation must not come at the expense of ethical responsibility or ecological integrity. The story of genetically modified mosquitoes should compel us to tread carefully, recognizing that solutions to global challenges must be as sustainable and thoughtful as the problems they aim to solve.
Sources:
- Emerging Mosquito Control Technologies | US EPA. (2024b, October 8). US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/regulation-biotechnology-under-tsca-and-fifra/emerging-mosquito-control-technologies#:~:text=In%20April%202020%2C%20EPA%20approved,mosquitoes%20at%20reducing%20local%20mosquito
News
His Family Voted to Support Deportation Plan. That Includes Him.

In a small town nestled in the foothills of Georgia’s Appalachian Mountains, Jaime Cachua lives a life that seems quintessentially American. He’s a devoted father, a trusted employee, and an active church volunteer. Yet, beneath this facade of normalcy lies a fragile reality—one shaped by political policies, shifting societal attitudes, and a precarious immigration status.
As a nation debates the fate of millions like Jaime, his story highlights the painful complexities of living as an undocumented immigrant in a place you’ve called home your entire life. What happens when the very community you’ve invested in begins to view you as an outsider? And how do you reconcile love for your family with fear of losing them forever?
Shattered Trust in Community
The story of Jaime Cachua, an undocumented immigrant in the United States, highlights the profound challenges faced by individuals in similar situations, particularly regarding trust within their communities. Cachua’s experience reflects a broader issue where undocumented immigrants often feel alienated and hesitant to engage with local institutions due to fear of exposure and potential deportation.
Studies have shown that perceptions of discrimination can significantly impact immigrants’ trust in political institutions and their sense of belonging. For instance, research published in the European Political Science Review indicates that experiences of discrimination are associated with lower levels of political trust and national belonging among non-Western immigrants.
Additionally, the fear of deportation and family separation contributes to the erosion of trust within immigrant communities. A study in the American Journal of Public Health found that local immigration enforcement policies can negatively affect the health and well-being of Hispanic/Latino immigrants, leading to increased distrust in health services and other institutions.
The Emotional Toll on Family
The looming threat of mass deportations under President-elect Donald Trump’s administration has cast a shadow over countless families, instilling fear and uncertainty about their futures. The emotional toll of potential separation is profound, affecting both parents and children in mixed-status households.
Research indicates that children who experience parental deportation are at heightened risk for emotional and behavioral issues, including sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, and academic challenges.
The sudden absence of a parent disrupts the child’s sense of security, leading to feelings of abandonment and trauma.
Parents, too, endure significant psychological distress. A study focusing on deported fathers revealed their profound frustration and helplessness at being unable to provide love, care, and support to their children from afar.
This separation strains familial bonds and can lead to long-term emotional scars for all involved.
In the case of Jaime Cachua, the fear of deportation has already begun to fracture his family life. His wife, Jennifer, is experiencing insomnia, and their children are afraid to go to school. Seeking guidance, Jaime turned to his father-in-law, Sky Atkins, who admitted, “I voted for Trump. I believe in a lot of what he says.” This revelation underscores the complex dynamics and emotional turmoil within families facing the threat of separation.
The anticipation of enforced family separations is causing widespread anxiety among immigrant communities. Many are taking legal precautions, such as seeking advance parole, to protect their family units. However, the uncertainty surrounding immigration policies continues to exacerbate stress and fear, impacting the mental health and well-being of both adults and children.
Caught Between Two Worlds

Navigating the complexities of undocumented status in the United States often places individuals in challenging positions, straddling the line between two distinct worlds. This dual existence is marked by the pursuit of the American dream and the constant fear of deportation, leading to a profound sense of alienation.
Sociologist Rubén G. Rumbaut describes this phenomenon as a “master status,” where undocumented individuals are primarily identified by their lack of legal status, overshadowing other aspects of their identity.
This status significantly influences their daily experiences, from employment opportunities to social interactions.
In the case of Jaime Cachua, a 33-year-old undocumented immigrant living in rural Georgia, this duality is evident. Despite spending nearly his entire life in the U.S., he faces the threat of deportation due to recent political shifts favoring mass deportation. His father-in-law, Sky Atkins, who supports stricter immigration policies, told Jaime, “I voted for Trump. I believe in a lot of what he says.”
This situation exemplifies the internal conflicts and societal pressures undocumented individuals endure, as they are caught between their established lives in the U.S. and the looming possibility of removal.
Studies indicate that such circumstances can lead to “acculturative stress,” manifesting as anxiety, depression, and a sense of alienation. This stress is exacerbated by the necessity to navigate between cultural identities, often resulting in psychological distress and challenges in social integration.
Legal Hurdles and Financial Strain
The case of Jaime Cachua, an undocumented immigrant in Rome, Georgia, exemplifies these struggles. His wife, Jennifer, has been “up all night on the computer, researching the intricacies of immigration law and trying to hire a lawyer,” despite their substantial debt.
Undocumented immigrants often face complex legal hurdles when seeking lawful status. Jaime’s best opportunity is a program for immigrants married to U.S. citizens who have resided in the country for at least ten years without criminal records.
However, navigating this process requires substantial legal assistance, which can be prohibitively expensive. A study in the Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health highlights that anti-immigration policies can adversely affect access to health services and overall health outcomes among undocumented immigrants, underscoring the broader implications of legal status.
Financial strain is a pervasive issue for undocumented families. Many work in low-wage jobs without access to employer-sponsored health insurance or benefits, leading to economic insecurity. Research indicates that undocumented immigrants are less likely to have health insurance, which exacerbates health inequities.
Additionally, the constant threat of deportation and associated legal costs can deplete family resources, causing significant stress and anxiety. A study in the Journal of Family and Economic Issues found that financial stress among undocumented immigrants is linked to poor mental health outcomes, highlighting the intersection of economic and psychological well-being.
A Fractured Community

The recent anti-immigrant sentiments in Rome, Georgia, have deeply fractured the community, leaving individuals like Jaime Cachua feeling alienated. Jaime, who has lived in the United States since he was 10 months old, now faces the possibility of deportation due to shifting political tides. His father-in-law, Sky Atkins, admitted, “I voted for Trump. I believe in a lot of what he says.” This revelation has strained familial bonds and trust within the community.
Studies indicate that sudden policy shifts and anti-immigrant rhetoric can erode social cohesion. Research on forced migration and social cohesion suggests that while general attitudes may remain unchanged, there can be a temporary increase in anti-immigrant violence, reflecting a decline in social cohesion.
In Rome, the pervasive anti-immigrant sentiment has led to a palpable sense of division. Jaime’s wife, Jennifer, expressed her frustration: “Why am I the one doing all of the work?” She had assumed that their marriage would resolve Jaime’s immigration status, but instead, they’ve encountered numerous obstacles and expenses.
Hope Amid Uncertainty
In the face of potential deportation, Jaime Cachua and his family grapple with significant legal and financial challenges. Their situation underscores the complexities of the U.S. immigration system and the personal toll it exacts on individuals and families.
Jaime’s best chance to become a legal U.S. resident was a new program for immigrants like himself—people married to U.S. citizens who had lived in the country for at least 10 years without committing any crimes. However, this program was recently struck down by a Trump-appointed federal judge, leaving Jaime with limited options.
Navigating the legal system is both daunting and expensive. Jaime and his wife, Jennifer, have been trying to hire a lawyer, even though they are thousands of dollars in debt. The costs associated with legal representation, application fees, and potential travel for immigration proceedings can be overwhelming for families already struggling financially.
Studies have shown that immigrants often face significant financial burdens when seeking legal status. According to the American Immigration Council, the average cost of obtaining legal status can range from $500 to $10,000, depending on the complexity of the case. These expenses can be prohibitive for many families, leading to difficult decisions and sacrifices.
In addition to legal fees, the potential loss of income is a pressing concern. Jaime’s temporary work permit, granted through the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) program, is under threat due to ongoing legal challenges and policy changes. Losing his work authorization would eliminate the family’s primary source of income, exacerbating their financial strain.
The uncertainty surrounding their legal status also affects their ability to plan for the future. Jennifer has been up all night on the computer, researching the intricacies of immigration law and trying to prepare for various outcomes. This constant state of vigilance takes an emotional toll and diverts time and energy from other aspects of family life.
Lessons from a Divided America
Jaime Cachua’s story is a stark reminder of the human complexity that lies behind immigration debates. His life, deeply rooted in Rome, Georgia, reflects the paradox of belonging to a community that questions his right to exist within it. Despite the emotional and financial toll, Jaime and his family demonstrate resilience in the face of an unforgiving system, holding onto hope and faith even as the odds seem insurmountable.
This journey illustrates the need for thoughtful immigration reform—policies that recognize the humanity of individuals like Jaime while addressing national concerns. Families such as his remind us that immigration isn’t just about statistics or laws; it’s about people—parents, children, and neighbors—whose lives are shaped by the decisions of others.
As the nation continues to grapple with its identity and policies, the question remains: Can a society balance sovereignty with compassion? The answer may lie in stories like Jaime’s, urging us to see the individual lives intertwined with these debates and challenging us to build a future where belonging is not conditional but inclusive.
Featured Image from Instagram @cachuanator
News
The Arctic Could Experience Its First Ice-Free Summer As Early As 2027

In the frozen silence of the Arctic, where ice has reigned for millennia, a dramatic transformation is underway. Scientists now predict that by the summer of 2027, the Arctic could be entirely ice-free—a milestone that would mark a profound shift not just for this remote region, but for the entire planet.
What does it mean when a natural shield that has reflected sunlight and stabilized global weather begins to vanish? How will ecosystems built on ice adapt to an ocean where none exists? And could the opening of new shipping routes and resource opportunities come at a cost too high to bear? This isn’t just about melting ice—it’s about unraveling the threads of a delicate global balance, with consequences that stretch from the Arctic Circle to cities half a world away.

Why the Arctic Is Losing Its Ice So Rapidly
The Arctic, often referred to as the planet’s “refrigerator,” is experiencing a rate of warming that far outpaces the rest of the globe—approximately four times faster, according to recent studies. This phenomenon, called Arctic amplification, is driven by a powerful feedback loop. As sea ice melts, it exposes darker ocean waters beneath, which absorb significantly more sunlight compared to the reflective ice. This increased absorption further warms the ocean, accelerating the melting process and creating a cycle that feeds on itself. This feedback loop isn’t just speeding up ice loss; it’s fundamentally altering the Arctic’s role as a global stabilizer of climate and weather systems.
Scientific research highlights the staggering scale of this change. The Arctic is losing an estimated 12.6% of its sea ice per decade, with some years seeing even greater losses. Historically, the idea of an ice-free Arctic seemed like a distant possibility—something that might occur closer to the end of the century. However, newer climate models, bolstered by observational data, predict that the summer of 2027 could witness a landmark event: the first ice-free Arctic season in recorded history. Defined as less than 1 million square kilometers of ice coverage, this shift would mark a dramatic turning point for the region and the planet.
The implications of this rapid ice loss extend far beyond the Arctic itself. The region serves as a crucial stabilizing force for the Earth’s climate, regulating global temperatures and influencing atmospheric systems. With the loss of this icy shield, global weather patterns could become increasingly erratic. The Arctic’s transformation signals more than just environmental change—it represents a fundamental disruption to the systems that have maintained Earth’s delicate balance for centuries. Understanding the reasons behind this unprecedented transformation is essential to prepare for its far-reaching consequences.
The Impact on Arctic Wildlife and Ecosystems
The Arctic’s dramatic transformation is pushing its wildlife and ecosystems to the brink of collapse. These regions, long defined by their icy landscapes, are losing the very foundation on which life depends, threatening the survival of species that have evolved to thrive in one of the most extreme environments on Earth.
Polar bears, the iconic symbol of the Arctic, are among the hardest hit. They rely on sea ice to hunt seals, their primary food source. However, as the ice melts earlier in the spring and forms later in the fall, their hunting grounds are disappearing. This forces polar bears to swim greater distances or venture onto land, where food is scarce, leading to malnutrition and dwindling populations. Similarly, marine mammals such as walruses and seals, which depend on ice for resting, breeding, and protection, are finding their habitats increasingly unstable. Without sufficient ice, they become more vulnerable to predators and face greater challenges in rearing their young.
The cascading effects of ice loss ripple through the Arctic ecosystem. Plankton, which thrive under sea ice and form the foundation of the marine food web, are declining as ice cover diminishes. This reduction in plankton affects fish populations, which in turn impacts seabirds and larger predators. On land, species like caribou and Arctic foxes are experiencing shifts in vegetation patterns, while warming temperatures invite competition from species migrating northward, disrupting the balance of these delicate ecosystems.

New Opportunities and Risks for Shipping and Resource Exploitation
The prospect of an ice-free Arctic is reshaping global economic and geopolitical landscapes. As sea ice recedes, previously inaccessible regions are opening up, presenting lucrative opportunities for shipping, resource extraction, and trade. However, these developments come with significant risks to the fragile Arctic environment and its ecosystems.
One of the most immediate impacts is the emergence of new shipping routes, such as the Northern Sea Route and the Northwest Passage. These routes offer dramatically shorter travel distances compared to traditional passages like the Suez or Panama Canals, reducing shipping times by thousands of miles. For industries, this means lower fuel costs and faster delivery times, making the Arctic an attractive corridor for global trade. However, increased shipping traffic poses environmental threats, including oil spills, underwater noise pollution, and disturbances to marine life. The Arctic’s unpredictable weather and limited infrastructure add further risks to navigation and safety.
Beyond shipping, the Arctic is home to vast reserves of untapped oil, natural gas, and rare minerals. As the ice melts, access to these resources becomes increasingly feasible, sparking a scramble among nations and corporations eager to capitalize on them. Countries with Arctic coastlines, such as Russia, Canada, and the United States, are intensifying their efforts to claim sovereignty over resource-rich territories. While this resource rush promises economic benefits, it raises critical environmental concerns. Extracting fossil fuels from the Arctic not only endangers local ecosystems but also perpetuates the cycle of global warming by adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
What This Means for Global Climate Action
The accelerating transformation of the Arctic stands as a stark call to action for global leaders, policymakers, and individuals alike. An ice-free Arctic by 2027 is not just a milestone; it is a glaring warning sign that the planet’s climate systems are veering toward uncharted and dangerous territory. Addressing this crisis requires immediate and coordinated efforts to mitigate its far-reaching consequences.
One of the clearest messages from the Arctic’s changes is the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The loss of sea ice amplifies global warming through feedback loops, creating a scenario where the planet warms faster than anticipated. This acceleration underscores the critical importance of international agreements such as the Paris Accord, which aim to limit global temperature rise to below 2 degrees Celsius. However, current global efforts are falling short, and the Arctic’s rapid decline serves as a reminder that climate goals must be not only ambitious but also enforceable and actionable.
Technological solutions also hold promise in combating the effects of climate change. Innovations such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems, renewable energy advancements, and geoengineering proposals are being explored as tools to slow warming and stabilize climate systems. Yet, these technologies come with their own set of challenges, from scalability to ethical considerations, emphasizing the need for a multifaceted approach that balances innovation with sustainability.
The Arctic’s plight also highlights the interconnected nature of the global climate system. The melting ice and its ripple effects—rising sea levels, intensified weather events, and ecological disruptions—demonstrate that no region is isolated from the impacts of climate change. This realization demands global cooperation, where nations set aside short-term interests to address the broader challenge of climate resilience.
Racing Against Time: The Arctic’s Last Stand
The Arctic’s journey toward an ice-free summer by 2027 is more than a climatic milestone—it’s a stark reminder of the profound shifts taking place on our planet. This transformation is reshaping weather systems, altering ecosystems, and presenting both opportunities and risks for global industries. Yet, at its core, it reflects humanity’s complex relationship with nature and the urgent need to act before the balance tips irreversibly.
From the fragile habitats of polar bears to the emergence of new shipping routes and the geopolitical scramble for resources, the Arctic’s changes resonate far beyond its icy expanse. It is a region that holds lessons for the entire world—lessons about the interconnectedness of climate, economy, and survival. The consequences of inaction are clear, but so too are the possibilities for innovation and cooperation if nations come together to prioritize sustainability over short-term gains.
The Arctic’s transformation is not just a story of loss; it is a call to rethink how we live, how we consume, and how we protect the planet. The ice may be vanishing, but the opportunity to preserve what remains—and to build a future defined by resilience and balance—remains firmly in our hands. It’s a race against time, and the stakes have never been higher.
Inspirational
Inspired By Chinese Technology, Class 12 Madhya Pradesh Student Develops Human Carrying Drone

In the world of cutting-edge technology, innovation often comes from unexpected places. In Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, a high school student is turning heads with a remarkable invention that has the potential to redefine personal mobility and aerial transport. Inspired by international advancements and driven by his own curiosity, this young creator has developed a drone that can do something truly extraordinary—carry a human passenger.
What makes this story even more captivating is not just the invention itself, but the challenges overcome and the ambitious dreams fueling it. With a humble beginning and grand aspirations, this creation is poised to inspire and innovate far beyond its starting point. Curious to know more about this groundbreaking achievement and the mind behind it?
The Birth of MLDT 01
In the evolving landscape of drone technology, the concept of human-carrying drones has transitioned from science fiction to tangible reality. Studies have demonstrated the feasibility of such drones, with prototypes capable of lifting significant weights. For instance, research published in the IEEE Xplore detailed a prototype designed to produce a static thrust of 140 kgf, sufficient to carry a person.
Against this backdrop of technological advancement, a remarkable story of innovation has emerged from Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh. Medhansh Trivedi, a Class 12 student at the Scindia School, embarked on an ambitious project to develop a human-carrying drone, drawing inspiration from Chinese drone technology. “I got the inspiration to make this drone after seeing the drones of China,” Medhansh shared, highlighting the global influence on his endeavor.
With a budget of approximately ₹3.5 lakh and a development period of three months, Medhansh’s creation, named MLDT 01, showcases his dedication and resourcefulness. The drone measures 1.8 meters in both length and width, featuring a compact design optimized for stability and performance. It is equipped with four motors commonly used in agricultural drones, providing a combined output of 45 horsepower. This configuration enables MLDT 01 to carry a person weighing up to 80 kilograms, reach speeds of 60 km/h, and sustain flight for up to six minutes.
Medhansh’s journey was not without challenges. Limited resources and the complexities of designing a human-carrying drone required perseverance and ingenuity. He credits his teacher, Manoj Mishra, for providing both technical assistance and motivation throughout the project. “My teacher Manoj Mishra has helped me a lot technically along with motivation to develop the drone,” Medhansh acknowledged, emphasizing the importance of mentorship in his success.

Image credits: Twitter @sauravyadav1133
Key Features and Performance
The MLDT 01 drone, developed by Class 12 student Medhansh Trivedi, showcases impressive technical specifications that highlight its potential in personal aerial transportation.
Technical Specifications:
- Dimensions: The drone measures 1.8 meters in both length and width, providing a stable platform for flight.
- Power Output: Equipped with four motors commonly used in agricultural drones, MLDT 01 boasts a combined power of approximately 45 horsepower, enabling it to lift significant weight.
- Payload Capacity: Designed to carry a person weighing up to 80 kilograms, making it suitable for personal transportation.
- Flight Duration and Speed: Capable of flying continuously for up to 6 minutes at a speed of 60 kilometers per hour, allowing for quick short-distance travel.
- Altitude Limitations: While theoretically able to reach altitudes up to 4 kilometers, current safety protocols restrict its operational height to 10 meters during test flights.
Safety Considerations:
Safety remains a paramount concern in the operation of human-carrying drones. The MLDT 01 is currently tested at a maximum height of 10 meters to mitigate risks during initial trials. Future iterations will likely incorporate advanced safety features, such as automated landing systems and enhanced structural integrity, to ensure passenger security.
Comparative Analysis:
In the broader context of drone technology, the MLDT 01 aligns with global advancements in personal aerial vehicles. For instance, the EHang 184, developed by the Chinese company EHang, is an autonomous aerial vehicle designed to carry a single passenger at speeds up to 100 km/h. While the EHang 184 offers longer flight times and higher speeds, the MLDT 01 represents a significant achievement in the Indian context, particularly given its development by a high school student with limited resources.
Recognition and Support
The innovative prowess of Medhansh Trivedi has garnered significant attention and commendation from prominent figures in India’s scientific and political arenas.
During the foundation day celebrations of Scindia School, Union Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia, who also serves as the school’s patron, alongside ISRO Chief S. Somanath, lauded Medhansh’s achievement. Their acknowledgment not only highlights the significance of Medhansh’s work but also underscores the potential impact of such innovations on India’s technological landscape.
A pivotal figure in Medhansh’s journey has been his teacher, Manoj Mishra, who provided both technical assistance and motivational support. Mishra observed, “With the aim of doing something different, he used to take information about new inventions.” This mentorship was instrumental in transforming Medhansh’s ambitious idea into a functioning prototype.
Medhansh’s accomplishment has resonated beyond academic circles, capturing the interest of local and national media. Publications have featured his story, emphasizing the blend of youthful innovation and practical application. Such coverage not only brings recognition to Medhansh but also inspires other young minds to pursue technological advancements.
Buoyed by the recognition and support, Medhansh is determined to advance his project further. He envisions transitioning the MLDT 01 into a hybrid model and developing drones for broader applications, including goods transportation and agricultural use. His ultimate goal is to establish an air taxi company and create affordable helicopters for public use. The encouragement from esteemed personalities and the media serves as a catalyst for these future endeavors.
Challenges and Vision for the Future
Embarking on the development of the MLDT 01 drone, Medhansh Trivedi encountered several challenges, from technical complexities to resource constraints. The project demanded a significant investment of time and finances, with approximately ₹3.5 lakh allocated over three months. Medhansh acknowledges the pivotal role of his mentor, Manoj Mishra, stating, “My teacher Manoj Mishra has helped me a lot technically along with motivation to develop the drone.”
Looking ahead, Medhansh envisions expanding the drone’s capabilities by transitioning to a hybrid model, aiming to enhance flight duration and efficiency. He articulates his broader aspirations: “In future, I will make drones useful for common people which can be used to carry goods, transport a person to another place and in agriculture.”
Medhansh’s ambition extends to establishing an air taxi company and developing affordable helicopters, reflecting his commitment to revolutionizing personal transportation and logistics. His journey underscores the importance of innovation, mentorship, and resilience in overcoming obstacles to achieve technological advancements.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LV18yyRZ5C
A Skyward Vision: Pioneering the Future of Drones
Medhansh Trivedi’s innovative journey with the MLDT 01 human-carrying drone is a beacon of creativity, resilience, and determination. From overcoming technical challenges to capturing the attention of prominent figures and media, his story is an inspiring reminder of what young minds can achieve with the right guidance and support.
IThis drone represents not only an individual’s achievement but also the possibilities for aerial technology to transform industries like transportation, agriculture, and logistics. With ambitions of creating hybrid drones, air taxis, and affordable helicopters, Medhansh is poised to push the boundaries of innovation even further.
As Medhansh continues to refine his creation and pursue his dreams, his story serves as a testament to the transformative power of ingenuity, mentorship, and a forward-thinking vision. The MLDT 01 is just the beginning—a launching point for a future where personal aerial transport becomes accessible to all.
News
Scientists Have Discovered a Second Hidden Core Inside Earth:

Imagine trying to solve a puzzle buried 3,000 miles beneath your feet, hidden within layers of molten rock and intense pressure. For centuries, scientists have believed Earth’s inner core—a dense, solid ball of iron and nickel—was the unwavering heart of our planet. But what if that core isn’t as solid as we thought? Recent discoveries suggest it might be more like a molten slurry, a mushy blend that defies long-held assumptions.
Could this revelation help unlock the secrets of Earth’s magnetic field, or even rewrite our understanding of how our planet functions? With seismic waves offering only glimpses into this mysterious realm, the truth about the Earth’s core is stranger—and squishier—than anyone could have imagined.

What is the Inner Core?
The Earth’s inner core has long been thought of as a dense, unyielding sphere of iron and nickel, buried over 3,000 miles beneath the surface. Measuring about 760 miles in radius, it’s often likened to a planet within a planet, surrounded by the liquid outer core. This inner core plays a critical role in sustaining Earth’s magnetic field, which shields us from harmful solar radiation and helps maintain the delicate balance of life on the surface.
Historically, scientists have portrayed the inner core as a solid, unwavering structure, contrasting with the turbulent liquid layer surrounding it. Its composition and behavior have been key to understanding the geodynamics of our planet. However, the reality may not be as straightforward as textbooks suggest. Recent findings challenge the long-standing belief in the core’s solidity, revealing a far more dynamic and complex nature.
The core is not just a static feature of the Earth but a living, evolving system. The interplay between its solid and liquid layers has profound implications for how the planet functions—implications we are only beginning to unravel. Could this newly uncovered “mushy” nature explain some of the enduring mysteries about Earth’s magnetic field? Scientists are now peering deeper into this hidden realm to uncover the answers.
A New Discovery: The ‘Mushy’ Core
For decades, the Earth’s inner core has been described as solid—its structure a dense, metallic core compressed under unimaginable pressure. However, groundbreaking research is challenging this view. Scientists now suggest that parts of the inner core may not be as rigid as previously believed. Instead, these areas could have a “mushy” consistency, resembling a mix of solid and liquid phases rather than a perfectly solid sphere.
This revelation emerged from seismic wave studies, which have long served as the primary tool for exploring the Earth’s depths. These waves, generated by earthquakes, travel at varying speeds depending on the material they pass through. Recent findings revealed unexpected variations in wave behavior as they moved through the inner core, suggesting the presence of a less uniform, partially fluid structure. As the researchers put it, their observations hint at a “complex internal structure” within the core.
What makes this discovery particularly intriguing is its implications for the Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetic field is generated by the interaction between the molten outer core and the supposedly solid inner core. If parts of the inner core are mushy or semi-liquid, this dynamic could influence the behavior of the magnetic field in ways we don’t yet fully understand. It raises questions about how the core has evolved over billions of years and what role this variability might play in the future stability of the magnetic field.
This shift in understanding isn’t just a minor adjustment to geological models. It’s a paradigm shift that forces scientists to rethink how the core interacts with the rest of the planet. The very foundation of how we understand Earth’s inner workings is being reexamined, pushing the boundaries of knowledge about what lies beneath our feet.

How Scientists Made This Discovery
The Earth’s core remains an enigma hidden beneath layers of rock and molten metal, making direct exploration impossible. Scientists instead rely on seismic waves—vibrations produced by earthquakes—to unravel its secrets. These waves change speed and direction as they travel through different materials, offering glimpses into the planet’s interior structure.
Recent seismic studies revealed unexpected variations in wave behavior as they passed through the inner core. These variations challenged the long-held belief that the core is a perfectly solid sphere of iron and nickel. Jessica Irving, a geophysicist at the University of Bristol, succinctly captured the excitement of this discovery: “The more that we look at it, the more we realize it’s not one boring blob of iron.” Instead, parts of the core appear to have a “mushy” texture—a blend of solid and liquid phases.
Seismic waves are particularly revealing because of their sensitivity to changes in density and composition. By analyzing wave speeds and their interactions with the core’s material, scientists identified regions where the core’s consistency didn’t match traditional expectations. According to Rhett Butler, a geophysicist at the University of Hawai‘i, these findings highlight the incredible complexity of the Earth’s interior: “We’re finding a whole new hidden world.”
This discovery underscores the power of seismic technology and the ingenuity of researchers who interpret these faint signals from deep within the Earth. By decoding these vibrations, scientists are uncovering a dynamic, multilayered core that challenges our understanding of planetary processes. These advancements also open the door to new questions about the role this variability might play in Earth’s magnetic field and its evolution over billions of years.
Implications of a ‘Mushy’ Core
The discovery of a mushy, partially liquid inner core isn’t just a scientific curiosity—it has profound implications for understanding the Earth’s magnetic field and its stability. The inner core, long thought to be a solid iron-nickel sphere, interacts with the outer core’s swirling molten metal to generate the magnetic field that protects the planet from harmful solar radiation. But what happens when parts of that supposedly solid core are revealed to be less stable?
According to scientists, the newfound variability within the inner core could influence the magnetic field’s behavior in ways we are only beginning to comprehend. “Having this mosaic of regions with different compositions, different phases, and different properties is just a natural consequence of the solidification process,” Jessica Irving explained. These irregularities may help scientists understand fluctuations in the magnetic field over time, including its periodic weakening and strengthening.
The discovery also raises questions about the evolution of the Earth’s core and its future. If the inner core is not entirely solid, how might this affect its cooling process? Could it alter the timeline for when the core will eventually freeze entirely, as some models predict? “The Earth’s core is not just a static lump of iron,” emphasized Rhett Butler. “It is dynamic and evolving, with layers interacting in ways we are only starting to appreciate.”
Moreover, this finding reshapes how scientists approach the study of Earth’s inner workings. It suggests that the core is more complex and variable than previously assumed, which could have ripple effects on how we model planetary processes, from plate tectonics to the magnetic field. These revelations are a reminder of just how much remains unknown about the world beneath our feet—and how every discovery brings us closer to unlocking Earth’s deepest mysteries.
What’s Next for Core Research?
The revelation of a mushy inner core has opened new doors for scientific inquiry, sparking questions about Earth’s most inaccessible layer. With seismic wave studies revealing complexities previously thought impossible, researchers are now focusing on refining their tools and techniques to gain even deeper insights. “Seismology is the key to peering into the Earth’s hidden layers,” said Jessica Irving, underscoring the importance of continued advancements in this field.
One key area of future research involves understanding how the inner core’s variability impacts Earth’s magnetic field. This dynamic shield is essential for protecting the planet from solar winds and cosmic radiation, yet its fluctuations remain poorly understood. Could the mushy regions of the core play a role in these magnetic anomalies? “We’re still piecing together the puzzle,” noted Rhett Butler, emphasizing the need for further exploration of the interplay between the inner and outer cores.
Additionally, scientists are exploring whether this new understanding of Earth’s core could have implications beyond our planet. By comparing Earth’s inner core to those of other celestial bodies, researchers may uncover universal principles about planetary formation and evolution. “Every new discovery here on Earth gives us a lens to look outward and understand other worlds,” Butler added.
Technological advancements will be crucial in this endeavor. From more sensitive seismometers to sophisticated computer models that simulate core dynamics, these tools will allow scientists to dive even deeper into the planet’s secrets. As the mysteries of the core continue to unravel, one thing is clear: the Earth’s heart is far more dynamic and intricate than anyone ever imagined. Each step forward not only reshapes our understanding of the ground beneath us but also redefines our place in the cosmos.
Revisiting the Heart of the Earth
The discovery of a mushy, partially liquid inner core challenges long-held assumptions about Earth’s most mysterious layer. Far from being a “boring blob of iron,” as Jessica Irving described it, the inner core is a dynamic, evolving structure that holds the key to understanding some of the planet’s most critical processes. From its role in generating the magnetic field to its influence on Earth’s long-term stability, the inner core is a reminder of just how little we truly know about the world beneath our feet.
This revelation not only reshapes our understanding of Earth’s interior but also opens new possibilities for exploring the hidden mechanics of planetary systems. With seismic waves as our primary tool, scientists are steadily unraveling the complex interplay between the inner and outer cores, revealing a planet that is anything but static.
Big Pharma
New York Hospital Charges A Young Woman $40 For Crying During Her Visit

The cost of healthcare in the United States has always been a hot-button issue, but every so often, a story emerges that leaves people questioning the boundaries of reason. One such story recently went viral, involving a young woman who was charged for something so seemingly ordinary that it shocked thousands online. This unexpected fee wasn’t for a test, a procedure, or even a consultation—it was for an emotional response. As the details unfolded, it became clear that this wasn’t just an isolated case but a window into the broader complexities and frustrations of navigating the American healthcare system.
The $40 Charge: What Happened?
In early 2022, Camille Johnson, a 25-year-old content creator from Brooklyn, New York, shared a startling experience involving her younger sister’s medical visit. Her sister, who had been grappling with a rare health condition, finally secured a doctor’s appointment. Overwhelmed by the situation, she shed a tear during the consultation. Later, when reviewing the itemized medical bill, they discovered a $40 charge labeled as a “brief emotional/behavioral assessment.” Camille expressed her frustration on Twitter, stating, “One tear in and they charged her $40 without addressing why she is crying, trying to help, doing any evaluation, any prescription, nothing.”
This incident is not isolated. A 2020 study published in JAMA found that 1 in 5 insured adults in the U.S. received an unexpected medical bill from an out-of-network provider in the past two years.
The public reaction to Camille’s tweet was swift and widespread, with many sharing similar experiences of unexpected medical charges. One user recounted being billed $1,902 for a pregnancy test labeled as “Women’s services,” while another mentioned a $44 fee for “skin to skin contact” after childbirth.
Understanding Emotional/Behavioral Assessments

The $40 charge labeled as a “brief emotional/behavioral assessment” on Camille Johnson’s sister’s medical bill corresponds to CPT code 96127. This code is defined as a brief emotional or behavioral assessment using standardized instruments, including scoring and documentation. It’s commonly used for screenings related to depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and substance abuse.
The implementation of CPT code 96127 aligns with the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which mandates that mental health services be included as essential benefits in all insurance plans. This initiative aims to ensure that mental health screenings are a routine part of medical care, promoting early detection and intervention for mental health conditions.
However, in the case of Johnson’s sister, the application of this code appears to have been misused. According to Johnson, her sister was not evaluated for any mental health conditions during the visit. She stated, “They did not evaluate her for depression or other mental illnesses, nor did they discuss her mental health with her.” This discrepancy highlights a potential issue where the code may be applied without the corresponding service being provided, leading to unexpected charges for patients.
A study published in the Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research emphasizes that while the ACA has expanded coverage for mental health services, the consistent and appropriate application of these services remains a challenge. Ensuring that patients receive the assessments they’re billed for is crucial for maintaining trust in the healthcare system.
The Broader Issue: Healthcare Transparency
A significant factor contributing to this opacity is the use of chargemasters—comprehensive lists of billable services and their prices maintained by healthcare providers. These lists are typically not disclosed to patients, leading to confusion and mistrust when unexpected charges appear on medical bills. As noted in a New Yorker article, the complexity and secrecy surrounding chargemasters have been criticized for contributing to the high costs of healthcare.
The lack of transparency in medical billing has tangible consequences. A study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that despite mandates for hospitals to publish pricing information, the data is often presented in formats that are not user-friendly, hindering patients’ ability to make informed decisions about their care.
The implications of opaque billing practices are profound. Patients may delay or forgo necessary medical care due to fear of unforeseen costs, potentially leading to worsened health outcomes. Moreover, unexpected medical bills can contribute to financial strain, with medical debt being a leading cause of bankruptcy in the United States.
Addressing these challenges requires systemic changes to promote transparency and rebuild trust between patients and healthcare providers. Implementing clear, accessible billing practices and ensuring patients are informed about potential costs upfront are essential steps toward a more equitable healthcare system.
The Public Reaction and Online Debate
The public reaction to Camille Johnson’s revelation about her sister being charged $40 for crying during a doctor’s appointment was swift and widespread. Many individuals shared their own experiences with unexpected medical charges, highlighting systemic issues within the U.S. healthcare system.
One Twitter user recounted, “I got charged over $2,000 for an emergency room trip for a nosebleed that wouldn’t stop. I had to wait so long, the nurse moved me into a room because I was bleeding all over the waiting room. Doc never saw me; it stopped bleeding before he arrived.”
Another individual shared, “My daughter was charged $44 for ‘skin-to-skin contact.’ In other words, when they flopped my grandson up onto her chest after the umbilical cord was cut. I guess the cheaper alternative was letting him fall on the floor?”
These personal accounts resonated with many, prompting discussions about the transparency and ethics of medical billing practices. The collective outrage underscored a growing demand for systemic reforms to address the financial burdens imposed on patients.
In response to the widespread attention, Camille Johnson emphasized the need for change, stating, “We need a drastic change in the healthcare industry, and I thought that sharing a real-life story online would be a good way to open up the conversation and help advocate for change.”
The online debate highlighted a pervasive sentiment: that the commodification of basic human experiences within the healthcare system is both ethically questionable and indicative of deeper systemic issues. As one commenter aptly put it, “Tell me you live in America without telling me that you live in America.”
Tips for Navigating Medical Bills
Navigating medical bills can be daunting, especially when unexpected charges arise. Here are some practical steps to help manage and potentially dispute such bills:
- Request an Itemized Bill: Always ask for a detailed breakdown of charges. This allows you to identify any discrepancies or unexpected fees, such as the $40 charge for a “brief emotional/behavioral assessment” in Camille Johnson’s sister’s case.
- Review Bills for Errors: Billing errors are not uncommon. Common mistakes include double billing, upcoding, or charges for services not rendered. A study in JAMA Health Forum highlights that self-advocacy in identifying and correcting these errors can lead to financial relief.
- Understand Your Insurance Coverage: Familiarize yourself with your insurance policy to know what services are covered and to what extent. This knowledge can help you spot charges that should have been covered by your insurer.
- Communicate with Healthcare Providers: If you identify an unexpected charge, contact the billing department of the healthcare provider. A respectful and clear inquiry can often resolve misunderstandings or errors. As noted by Patient Fairness, preparing and sending a letter of dispute promptly can obligate the provider to address your concerns.
- Negotiate Bills: Don’t hesitate to negotiate medical bills. Many providers offer discounts for prompt payment or can set up interest-free payment plans to ease financial strain.
- Seek Financial Assistance: Hospitals and clinics often have financial assistance programs for patients facing financial hardships. Inquire about eligibility to reduce your medical expenses.
- Document All Communications: Keep detailed records of all interactions with healthcare providers and insurance companies, including dates, names of representatives, and summaries of discussions. This documentation can be crucial if disputes escalate.
- Consult a Patient Advocate: If the process becomes overwhelming, consider seeking help from a patient advocate. They can assist in understanding bills, disputing charges, and negotiating with providers. Patient advocates can improve health outcomes and prevent errors by facilitating communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- Be Aware of Legal Protections: Familiarize yourself with laws designed to protect patients from unfair billing practices, such as the No Surprises Act, which aims to prevent unexpected medical bills.
- Stay Informed and Proactive: Regularly review medical statements and Explanation of Benefits (EOBs) from your insurer. Prompt attention to discrepancies can prevent minor issues from becoming significant financial burdens.
A Call for Compassion in Healthcare
The story of Camille Johnson’s sister being charged $40 for crying during a medical visit has become a symbol of the broader issues plaguing the American healthcare system. From a lack of transparency in billing practices to unexpected fees that exacerbate financial and emotional burdens, the challenges patients face are undeniable.
At its core, healthcare should prioritize empathy and patient well-being. The commodification of basic human experiences, such as an emotional response, highlights the urgent need for systemic reforms. Greater transparency, clear communication, and ethical billing practices are essential steps toward restoring trust and dignity in healthcare.
As public outrage over stories like these grows, it’s clear that change is possible, but it requires collective action. Patients, advocates, and policymakers must work together to ensure that the healthcare system reflects its ultimate purpose: to heal, support, and care for those in need, without undue financial strain or unnecessary distress. This story serves as a reminder that every voice counts in the fight for a more compassionate and transparent system.
Inspirational
13-Year-Old Owen Burns Saved His Sister From A Kidnapper Using A Slingshot, Striking The Attacker With A Marble.

It’s not every day that a slingshot—a tool most often associated with childhood mischief—becomes the weapon of choice in a life-or-death situation. Yet, in Michigan, a 13-year-old boy named Owen Burns turned a simple toy into a tool of heroism, saving his younger sister from a would-be abductor.
This extraordinary act raises a question: how far will someone go to protect the ones they love? For Owen, the answer was instinctive and immediate. Armed with quick thinking, a marble, and a deep sense of responsibility, he transformed a terrifying moment into a triumphant one. His story is a striking reminder that courage doesn’t always come in the form of elaborate plans or adult intervention—it can spring from the most unexpected places, even the hands of a young teenager in the quiet heart of Michigan.
The Harrowing Moment
The quiet suburban neighborhood in Alpena Township, Michigan, was no stranger to the sounds of children playing and families going about their daily lives. But one afternoon, that serenity shattered when an unknown man emerged from the shadows, attempting to abduct Owen Burns’ 8-year-old sister. She had been outside gathering mushrooms near their backyard when the stranger struck, covering her mouth and attempting to drag her away.
Inside the house, Owen had been playing video games when he heard his sister’s muffled screams. Glancing out the window, he saw the horrifying scene—a stranger pulling his sister toward the woods. “I’m like freaking out,” Owen later said, recalling the intense moment. “It just felt like I was scared, and I had … to do.”
Faced with a split-second decision, Owen acted on instinct. Grabbing his slingshot, a favorite toy that had never been intended for such dire use, he aimed and fired. “Cause if I didn’t … she would’ve been taken away or … worse,” he said, reflecting on the gravity of the situation.
The Heroic Act
When Owen Burns grabbed his slingshot, he didn’t have time to calculate his aim or second-guess his decision. Fueled by fear and determination, he loaded it with a marble, pulled back, and released. The marble struck the would-be kidnapper squarely in the head, forcing him to stumble. Without missing a beat, Owen fired a second shot, this time hitting the man in the chest.
The accuracy and force of the strikes were enough to halt the attack, giving Owen’s sister the chance to break free and run to safety. The kidnapper, caught off guard by the unexpected defense, turned and fled into the woods.
Owen’s quick thinking and unusual weapon of choice became the difference between disaster and rescue. As his family later recounted, this simple slingshot, often used for playful target practice, had become a tool of extraordinary heroism. Law enforcement officials were equally impressed. State police spokesperson Lt. John Grimshaw remarked, “What he did also helped us to identify who the suspect was, because obviously he had injuries from getting hit with a slingshot.”
The bravery Owen displayed in those critical moments not only protected his sister but also left a literal mark on the attacker that would lead to his eventual capture.
The Attacker’s Capture
Thanks to Owen’s quick thinking and decisive action, the attacker didn’t just flee but also left behind crucial evidence—visible injuries inflicted by the slingshot. Authorities quickly mobilized after receiving the family’s urgent 911 call, immediately launching a search for the suspect. Owen’s sister provided critical details about the man who had attempted to abduct her, and the police combined this description with the injuries caused by Owen’s precise strikes to narrow down their suspect.
The attacker, a 17-year-old male, was identified and apprehended not long after the incident. He had been hiding nearby, trying to avoid detection. The bruises on his head and chest, along with the eyewitness account from the Burns family, solidified his involvement in the crime. He now faces multiple serious charges, including attempted kidnapping and assault, underscoring the gravity of the situation.
The swift capture of the suspect brought an overwhelming sense of relief to the Burns family and the local community. For a neighborhood known for its quiet and safety, this audacious daylight crime was a sobering reminder of the unpredictability of danger. Yet, it was also a moment to celebrate Owen’s bravery and resourcefulness in preventing what could have been a devastating outcome.
Owen’s actions not only ensured his sister’s safety but also played a pivotal role in ensuring that justice was served. His ability to think clearly in a moment of panic demonstrates the profound impact of courage and presence of mind, even in the hands of a young teenager. The story quickly became a source of inspiration for the local community and beyond, reminding everyone of the power of standing up against danger when it matters most.

Image Credit: https://www.youtube.com/@InsideEdition
The Hidden Reality of Child Abductions
Owen’s story is remarkable, not only because of his bravery but because it sheds light on an unsettling reality: attempted child abductions often happen in seemingly safe and familiar settings. According to the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children, many child abduction attempts occur near the victim’s home or a place they frequent. This underscores a critical need for awareness, even in neighborhoods considered secure.
What makes cases like this particularly chilling is the speed at which such incidents unfold. Experts estimate that the first few minutes of an attempted abduction are the most critical for determining the outcome. In Owen’s case, his quick intervention disrupted the kidnapper’s plan before it could escalate, illustrating just how decisive action can alter the course of events.
While public perception may focus on “stranger danger,” it’s important to recognize that many abduction attempts involve individuals familiar to the victim. This case, involving a stranger, is a sobering reminder that vigilance is always necessary, regardless of circumstances. Understanding how abductions occur and teaching children how to respond to unusual situations are key steps in reducing risks.
Beyond awareness, stories like Owen’s also highlight the importance of strong community ties and open communication within families. Regular conversations about safety, such as knowing how to seek help or recognizing suspicious behavior, empower children to act in critical moments. As Owen’s story demonstrates, even a young teenager can make a life-saving difference with the right instincts and the willingness to act.
The Power of Community and Shared Responsibility
Owen’s story is not just about individual heroism—it’s a call to action for communities to come together in protecting their most vulnerable members. Incidents like these highlight the importance of a collective approach to safety, where neighbors, schools, and local organizations all play a role in creating an environment that prioritizes children’s well-being.
Communities that are proactive in fostering safety and vigilance are less likely to experience such crimes. Simple measures, such as neighborhood watch programs, improved lighting in shared spaces, and awareness campaigns, can significantly reduce risks. It’s not about fostering paranoia but about cultivating a culture where people are attentive to one another and willing to step in when something feels off.
Schools, too, are critical hubs for instilling safety education. Programs that teach children how to identify suspicious behavior, seek help, and stay aware of their surroundings are invaluable. Partnerships between schools, local law enforcement, and parent organizations can amplify these efforts, ensuring that children are equipped with practical tools and knowledge.
At the heart of this story is the undeniable truth that no one is alone in safeguarding their community. Owen’s actions demonstrate how even the smallest acts of vigilance—whether by a teenager, a concerned neighbor, or a passerby—can have ripple effects that strengthen the safety net for everyone. His bravery is a reminder that we all share responsibility for looking out for one another, and that collective awareness can be a powerful deterrent to those who seek to harm.

Image Credit: https://www.youtube.com/@ABC7
A Reminder of Courage and Responsibility
Owen Burns’ story is more than just a tale of bravery—it’s a testament to the extraordinary capabilities of ordinary individuals in the face of danger. His quick thinking and courageous actions not only saved his sister but also served as a powerful reminder of how critical moments can define us.
This event has rippled far beyond Alpena Township, inspiring countless people to reflect on the importance of awareness, preparation, and community vigilance. It reminds us that heroism often comes without warning and from unexpected places, proving that even the simplest tools—like a slingshot—can become instruments of justice in the right hands.
As we celebrate Owen’s courage, we are reminded of the broader lessons his story teaches: the need for collective responsibility, the power of instinct, and the importance of standing up against harm, no matter the odds. In a world that often feels unpredictable, stories like this ignite hope, showing that resilience and love can triumph over fear.
The quiet Michigan town where this remarkable event unfolded will surely never forget what happened, nor will those who hear this story. Owen’s actions are a call to each of us to remain vigilant, prepared, and willing to act—not just for our loved ones but for the greater good of our communities.
Animals
Hunter Killed After Shot Elephant Falls Over And Crushes Him

In the vast and untamed wilderness of Africa, the line between predator and prey can blur in unexpected ways. For one seasoned hunter, a routine expedition took a shocking and ironic turn when nature struck back with a force no one could have predicted. What began as a pursuit of big game ended in tragedy, leaving many to question the morality of hunting and the unpredictable power of the wild.
What happened that day serves as a stark reminder of the risks hunters face—and the lengths animals will go to defend their own. But the full story holds more than just drama; it raises deeper questions about humanity’s relationship with the natural world.
The Incident: When the Hunter Becomes the Hunted
In May 2017, Theunis Botha, a seasoned 51-year-old South African big game hunter, led a group near Zimbabwe’s Hwange National Park—a region previously spotlighted by the 2015 killing of Cecil the Lion. During this expedition, the hunters unexpectedly encountered a breeding herd of elephants, known for their protective and unpredictable nature.
As the group approached, three elephant cows charged directly at them. Botha responded by firing shots to deter the advancing animals. However, a fourth cow launched a surprise attack from the side, lifting Botha with her trunk. In an attempt to rescue him, a fellow hunter shot the elephant, resulting in her immediate collapse onto Botha, fatally crushing him.
Botha was renowned for pioneering European-style “Monteria hunts” in South Africa, utilizing packs of hounds to drive game towards hunters—a method traditionally reserved for smaller animals but adapted by Botha for larger predators like lions and leopards.
This tragic event underscores the inherent dangers of big game hunting, even for the most experienced individuals. It also highlights the unpredictable nature of wildlife, especially when animals perceive a threat to their young. Studies have shown that such encounters can lead to heightened stress responses in wildlife, potentially increasing the likelihood of aggressive defensive behaviors.
Nature’s Retaliation: A Rare Reality

Image credits: Twitter @JimKirstin51355
The tragic demise of Theunis Botha, crushed by an elephant during a hunt, underscores the unpredictable and perilous dynamics between humans and wildlife. While such fatal encounters are uncommon, they highlight instances where animals, acting on instinct, turn the tables on their pursuers.
In a similar incident, Argentine hunter José Monzalvez was trampled to death by an elephant during a hunting expedition in Namibia. As Monzalvez prepared to shoot, the elephant charged, leading to his untimely death.
These events illustrate the inherent risks of big game hunting, where the hunter can swiftly become the hunted. Elephants, known for their intelligence and strong social bonds, exhibit protective behaviors, especially when their young are threatened. Their size and strength make any defensive action potentially lethal.
Beyond elephants, other wildlife has also retaliated against human threats. For instance, in Alaska, a hunter was attacked by a brown bear, leading to a life-threatening situation. Such encounters emphasize the unpredictability of wildlife and the potential dangers faced by those who venture into their habitats.
The Controversy of Big Game Hunting
The tragic death of Theunis Botha has reignited debates surrounding big game hunting, a practice that elicits strong opinions on both ethical and conservation fronts.
Ethical Considerations
Critics argue that trophy hunting is morally indefensible, viewing it as the killing of animals for sport rather than necessity. Organizations like PETA contend that such practices inflict unnecessary suffering on wildlife, with the pleasure derived by hunters failing to justify the harm caused. The League Against Cruel Sports echoes this sentiment, asserting that even when targeting non-endangered species, the act remains unjustifiable. They also challenge the purported economic benefits, labeling them as insufficient grounds for perpetuating inhumane activities.
Conservation Implications
Proponents of trophy hunting often claim it contributes to conservation efforts by generating revenue for wildlife preservation and local communities. However, studies challenge this narrative. Research published in One Earth indicates that the impact of recreational hunting on biodiversity and livelihoods is complex, with findings suggesting that a single characterization of its impact on conservation is necessarily simplistic.
Furthermore, evidence suggests that trophy hunting can adversely affect animal populations. Targeting the most robust individuals for trophies may lead to genetic and social disruptions within species. For instance, removing dominant males can destabilize social structures and impede reproductive success, potentially accelerating population declines.
Economic Perspectives
The economic justification for trophy hunting is also under scrutiny. Reports indicate that the financial contributions from such activities to local economies are minimal. A 2017 study by Economists at Large found that trophy hunting accounted for less than one percent of tourism revenue in eight African countries. Additionally, concerns about government corruption suggest that funds generated may not effectively support conservation initiatives.
Public Sentiment
Public reaction to Botha’s death has been polarized. While some express condolences to his family, others view the incident as a manifestation of nature’s retribution against a practice they deem unethical. This dichotomy reflects a broader societal debate over the legitimacy and consequences of big game hunting.

A Bigger Picture: The Consequences of Trophy Hunting
The tragic death of Theunis Botha has reignited discussions about the broader implications of trophy hunting on wildlife conservation, ethical considerations, and economic impacts.
Proponents of trophy hunting argue that it can contribute to conservation efforts by providing financial incentives to preserve wildlife habitats. For instance, in Namibia, regulated hunting has been associated with increases in certain wildlife populations, such as the mountain zebra, which grew from 1,000 in 1982 to 27,000 in 2014.
However, studies have shown that poorly managed trophy hunting can lead to negative ecological impacts, including altered age and sex structures within animal populations, social disruption, and even population declines. For example, selective hunting of male African lions has been linked to increased infanticide and social instability within prides.
While trophy hunting generates revenue, its economic significance is often overstated. A report by Economists at Large found that trophy hunting contributes less than 2% of overall tourism revenues in most African countries. Additionally, concerns have been raised about the equitable distribution of these funds, with limited benefits reaching local communities.
Ethical opposition to trophy hunting centers on the morality of killing animals for sport. Critics argue that it is unethical to take the life of a sentient being for recreation, regardless of any purported conservation benefits. This perspective is supported by animal welfare organizations that advocate for non-lethal conservation methods.
The debate over trophy hunting continues to evolve. In 2024, the UK proposed the Hunting Trophies (Import Prohibition) Bill, aiming to ban the import of hunting trophies. However, an Oxford-led study concluded that such a ban could cause more harm than good for the species it intends to protect, suggesting that a nuanced approach is necessary.
The Price of Trophy Hunting
The tragic death of Theunis Botha serves as a stark reminder of the unpredictability of nature and the consequences of human interference with wildlife. While some see the incident as a harsh act of nature’s justice, others view it as an unfortunate yet inevitable risk of big game hunting.
This story transcends one man’s fate; it reignites critical discussions about the ethical, ecological, and economic dimensions of trophy hunting. As wildlife populations face increasing pressures from habitat loss, poaching, and hunting, the need for more sustainable, non-lethal conservation methods grows stronger.
In a world where wildlife tourism generates far more revenue and preserves animals in their natural habitats, perhaps it’s time to reconsider humanity’s relationship with nature—not as a conqueror but as a guardian. For every action we take against wildlife, nature reminds us, in its own powerful way, that the balance is fragile, and the consequences are real.
Featured Image from Youtube @TheYoungTurks
Animals
Dinosaur Legs Grown On Genetically Modified Chicken Embryos In World First

Imagine holding a tiny, chirping creature in your hands, knowing it carries the echoes of a 66-million-year-old predator. Modern birds, from backyard sparrows to majestic eagles, are the closest living relatives of dinosaurs—a fact that has fascinated scientists and the public alike. But what if we could go beyond studying fossils and feathers to glimpse the very mechanics of this ancient connection?
In a groundbreaking experiment, researchers have managed to grow dinosaur-like legs on chicken embryos, bringing us one step closer to uncovering the evolutionary mysteries that link the prehistoric giants to today’s avian species. This scientific breakthrough not only challenges the boundaries of genetic research but also raises profound questions about the extent to which we can—and should—reverse-engineer evolution.

The Experiment: Bridging the Gap Between Birds and Dinosaurs
Modern birds are more than just distant cousins of dinosaurs—they are, in fact, their evolutionary descendants. This connection is well-documented, with shared anatomical features like hollow bones and three-toed limbs. However, a team of researchers led by João Francisco Botelho decided to push the boundaries of this relationship by exploring what happens when dormant dinosaur-like traits are reactivated in chicken embryos.
By manipulating the genetic mechanisms responsible for limb development, scientists successfully grew chicken embryos with fibula bones resembling those of theropod dinosaurs, such as Velociraptor. The fibula, a tubular bone extending from the knee to the ankle, was a prominent feature in dinosaurs but has since evolved into a shorter, splinter-like structure in modern birds.
The team targeted a specific gene, Indian Hedgehog (IHH), to achieve this transformation. By inhibiting IHH signaling during embryonic development, the researchers prevented the fibula from shortening, enabling it to maintain its dinosaur-like tubular shape. Their findings, published in the journal Evolution, offered profound insights into how minor genetic adjustments can evoke ancient anatomical traits.
This groundbreaking experiment not only demonstrates the power of genetics to illuminate evolutionary history but also highlights the intricate interplay between biology and the passage of time. Yet, it also raises important questions: How far can scientists ethically go in resurrecting traits from the past? Could experiments like these risk crossing boundaries in our pursuit of knowledge?
The Role of the Fibula: A Key Piece of the Puzzle
The fibula, a long bone in the lower leg, has undergone significant changes over the course of evolution. In theropod dinosaurs, this bone extended fully from the knee to the ankle, forming a robust, tubular structure essential for their locomotion and strength. In modern birds, however, the fibula has diminished, becoming short and splinter-like, no longer reaching the ankle.
In their groundbreaking study, researchers successfully manipulated chicken embryos to regrow fibula bones that resembled those of their dinosaur ancestors. By targeting specific genetic pathways, they prevented the typical shortening process that occurs during bird development, enabling the bone to retain its ancestral, dinosaur-like form.
This research highlights how genetic manipulation can reveal the evolutionary pathways that connect species. The restored fibula not only bridges the physical gap between dinosaurs and birds but also demonstrates the genetic potential of living organisms to express ancient traits. Such findings provide a window into the evolutionary process, revealing how small genetic changes can result in profound anatomical shifts over millions of years.
By focusing on the fibula, scientists have unearthed a fascinating piece of the evolutionary puzzle, shedding light on how traits from ancient species remain embedded in their modern descendants. This discovery sparks questions about what other dormant characteristics might be unlocked in the future, offering endless possibilities for understanding the biology of the past.

The Implications: What This Means for Science
This experiment marks a pivotal moment in the study of evolutionary biology, providing a tangible connection between the prehistoric world and modern-day species. By reactivating dormant genetic traits, researchers have demonstrated how small changes in developmental pathways can recreate anatomical features that have been absent for millions of years. This is more than a glimpse into the past—it’s a roadmap for understanding the genetic mechanisms that drive evolution.
The study also opens doors to new possibilities in the field of paleontology. Fossils have long been the primary source for understanding extinct species, but experiments like this allow scientists to explore evolution in real-time. By studying the genetic underpinnings of traits like the fibula, researchers can infer not only how certain physical characteristics evolved but also why they changed, shedding light on the pressures and adaptations that shaped ancient species.
Beyond evolutionary biology, this research could have broader implications for genetic science. The ability to modify developmental processes might one day help address congenital disorders or guide regenerative medicine by reactivating dormant genes. However, these advances are accompanied by complex ethical questions, particularly about the potential misuse of such techniques for purposes beyond scientific discovery.
While the idea of “de-extincting” traits from ancient species might sound like science fiction, this study brings us closer to the reality of reawakening evolution’s long-buried secrets. It challenges us to think about the boundaries of genetic research and the responsibilities that come with wielding such transformative tools. With every step forward, the line between possibility and limitation continues to blur, making the journey as exciting as it is thought-provoking.
Criticisms and Ethical Questions: Drawing the Line
While the success of this experiment is groundbreaking, it also raises significant ethical and scientific concerns. Manipulating the genetic makeup of organisms, particularly in their embryonic stages, can be seen as venturing into morally complex territory. Critics argue that experiments like these blur the line between scientific discovery and tampering with nature, sparking debates about how far scientists should go in altering life’s evolutionary course.
One of the primary concerns is the potential misuse of such technologies. While the study’s intent was to understand evolutionary processes, the same techniques could theoretically be applied to areas less focused on advancing knowledge, such as creating genetically altered organisms for non-scientific purposes. The ethical implications of manipulating genetic traits to revive characteristics from ancient species demand careful regulation and oversight.
There are also practical risks. Genetic modifications, even at the embryonic stage, might produce unforeseen consequences, not just for the organism itself but potentially for ecosystems and biodiversity if such traits were to persist or spread. Critics emphasize the importance of considering long-term impacts before exploring applications that go beyond controlled experimental settings.
Despite these concerns, proponents argue that the value of such research outweighs its risks when conducted responsibly. Studies like this provide critical insights into evolutionary biology, offering knowledge that could have implications for medicine, conservation, and our understanding of life’s history. However, striking a balance between scientific ambition and ethical responsibility is key to ensuring these advances are both meaningful and sustainable.
The Future of Evolutionary Research: What Lies Ahead?
This study is not just a look back at the past—it sets the stage for transformative research in evolutionary biology and genetics. By reactivating dormant traits in chicken embryos, scientists have shown that evolution leaves behind a genetic blueprint, one that can be studied, manipulated, and potentially applied in ways we are only beginning to understand.
One promising avenue lies in studying other dormant traits found in modern species. Traits like vestigial structures—appendices, tailbones, or even unused muscles—could hold clues to how organisms adapted to survive across millennia. These investigations could help refine our understanding of natural selection, adaptation, and extinction, providing insights into why certain traits persisted or vanished.
Additionally, this research offers practical applications beyond evolutionary study. By learning to manipulate genes that control developmental processes, scientists could uncover breakthroughs in regenerative medicine. For example, reactivating dormant genes might help regrow damaged tissues or reverse genetic conditions that have long been considered untreatable. While these ideas are still in the early stages, the potential for significant medical advancements is undeniable.
However, the road ahead isn’t without challenges. Ethical considerations will remain at the forefront of such research, as society grapples with the implications of modifying traits or even reviving extinct ones. Strict regulation and transparent dialogue between the scientific community and the public will be essential to ensuring these innovations serve humanity responsibly.
Evolution’s Living Legacy
The successful growth of dinosaur-like legs in chicken embryos represents more than just a scientific milestone—it’s a profound reminder of the unbroken connection between the distant past and the present. By unlocking genetic blueprints that have lain dormant for millions of years, researchers have provided a glimpse into the evolutionary mechanisms that shaped the world as we know it.
This experiment doesn’t just challenge our understanding of biology; it redefines the possibilities of genetic research. It opens doors to further explore the deep ties that link all species and offers new ways to study how life evolves and adapts. Yet, it also highlights the fine balance between curiosity and responsibility, as advancements in genetic science bring with them complex ethical dilemmas.
As we look to the future, studies like this compel us to question the very fabric of evolution. What other secrets lie hidden within the genomes of living organisms? How might this knowledge reshape our understanding of life’s origins and its potential paths forward?
News
Maps Show The Antarctic Is Turning Green With Plant Life – A Troubling Sign For The Planet

Antarctica, the coldest and most remote continent on Earth, has long been synonymous with vast, pristine sheets of ice and desolate, frozen landscapes. But what if the very image of this icy wilderness is beginning to melt—quite literally? In a striking turn of events, scientists have observed green patches spreading across its surface, a phenomenon driven by warming temperatures. This transformation, while visually unexpected, paints a troubling picture for our planet’s future.
Over the past few decades, Antarctica has experienced some of the fastest warming rates on the planet, with certain regions seeing temperatures rise by nearly 3°C. With these shifts, once-hostile environments are becoming fertile grounds for moss and algae to thrive. For a place once considered too extreme for vegetation, the sudden greening isn’t just a curiosity—it’s a harbinger of profound ecological shifts. What does this mean for one of the planet’s most fragile ecosystems, and how does it ripple into global climate systems?

What’s Causing the Antarctic to Turn Green?
The once-icy expanse of Antarctica is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven primarily by climate change. Rising global temperatures are the key factor, with the Antarctic Peninsula experiencing some of the fastest warming rates on the planet. Warmer conditions are lengthening the summer months, creating an environment where moss and algae can thrive.
According to scientists, algae blooms, often referred to as “green snow,” are becoming increasingly common. These blooms are linked to melting snow and ice, which create pools of nutrient-rich water where microscopic organisms can flourish. With temperatures climbing and ice receding, these conditions are spreading further across the continent, allowing plant life to establish a foothold in areas that were once entirely inhospitable.
Adding to the problem is the role of melting ice itself. As snow and ice retreat, darker surfaces like exposed ground and water absorb more sunlight, amplifying the warming effect in a feedback loop. This process, known as the albedo effect, not only encourages more plant growth but also accelerates the melting of glaciers—an alarming cycle with far-reaching implications for global sea levels.
This greening of Antarctica is not a natural adaptation or a sign of resilience. Rather, it’s a symptom of the profound impact humans are having on the planet, forcing even its most remote ecosystems to change in ways that could have devastating consequences.
How Scientists Mapped the Green Spread
Uncovering the greening of Antarctica required a combination of cutting-edge technology and meticulous research. Scientists employed satellite imagery and on-the-ground observations to map the spread of plant life across the continent. These tools allowed researchers to pinpoint areas where moss and algae have flourished, offering a detailed view of how the icy wilderness is evolving.
“The plants we find on the Antarctic Peninsula – mostly mosses – grow in perhaps the harshest conditions on Earth,” explained Dr. Thomas Roland, an environmental scientist from the University of Exeter. Despite these extreme conditions, mosses are now colonizing areas that were once completely covered in snow and ice.
One study, conducted by a team from the University of Cambridge and the British Antarctic Survey, used satellite data to identify “green snow” algae blooms across the Antarctic Peninsula. The research revealed that these blooms are not only growing larger but also appearing in new areas as temperatures rise. Their findings were compiled into detailed maps, showcasing how climate change is reshaping this fragile ecosystem.
“The landscape is still almost entirely dominated by snow, ice, and rock, with only a tiny fraction colonized by plant life. But that tiny fraction has grown dramatically – showing that even this vast and isolated ‘wilderness’ is being affected by anthropogenic climate change,” Dr. Roland emphasized. These maps provide a critical baseline for monitoring future changes and understanding how warming temperatures are transforming one of the world’s most remote regions.

Why This Green Growth Is a Warning, Not a Win
At first glance, the sight of greenery in Antarctica might seem like a curious or even positive development. After all, plant life is often associated with ecosystems thriving. But in this case, the rapid growth of moss and algae is a stark warning about the consequences of climate change—and the implications are far from positive.
One of the most alarming impacts is how this vegetation affects the albedo effect, a process where the Earth’s surface reflects sunlight. As green algae and moss spread, they darken the surface, absorbing more heat and accelerating ice melt. This creates a vicious cycle, where warmer temperatures lead to more plant growth, which in turn speeds up glacial melting.
Dr. Andrew Gray, a researcher involved in the study, explained, “As the snow melts, it creates the water algae need to grow, which then leads to more melting as the algae darken the surface.” This chain reaction could have significant consequences for global sea levels, as Antarctic ice is a major buffer against rising oceans.
The introduction of more vegetation also disrupts the region’s delicate ecosystem, which has evolved over millennia to exist with minimal organic matter. The greening of Antarctica underscores the urgency of addressing climate change before its effects cascade further into more fragile systems worldwide.
Impacts Beyond Antarctica
The greening of Antarctica is not just an isolated environmental shift; its effects ripple far beyond the continent itself. As one of Earth’s primary climate stabilizers, Antarctica plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of global systems. The changes taking place there—especially the rapid ice melt—could set off a chain reaction with serious consequences for the rest of the world.
One of the most immediate and alarming impacts is the rise in global sea levels. Antarctica holds about 60% of the planet’s fresh water in its ice sheets, and as these melt at an accelerating rate, millions of people in coastal regions face the threat of flooding. Even small increases in sea levels can lead to storm surges, erosion, and the displacement of entire communities.
Beyond sea level rise, Antarctica’s transformation can disrupt global weather patterns. The continent’s icy expanse helps regulate ocean currents and wind systems, which are critical to the planet’s climate stability. As the ice recedes and more vegetation spreads, it alters the thermal and salinity gradients in the surrounding oceans. This can weaken vital currents, like the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, and affect weather systems worldwide.
Another concern is how these changes might influence carbon cycles. While algae and moss absorb carbon dioxide during growth, the overall warming and ice loss they contribute to releases far greater amounts of greenhouse gases trapped in the ice and soil. This exacerbates global warming, creating further challenges for already vulnerable ecosystems around the world.
The greening of Antarctica is a clear signal that the impacts of climate change are interconnected, transcending borders and ecosystems. What happens in the icy south ultimately affects us all, underscoring the urgent need for global action to mitigate these cascading effects.
What Can Be Done to Slow This Down?
The rapid greening of Antarctica is a visible symptom of a much larger issue: accelerating climate change. Addressing this crisis requires collective, global action to mitigate its root causes and prevent further damage to the planet’s most fragile ecosystems. While reversing the current trajectory may seem daunting, there are actionable steps that can help slow the changes impacting Antarctica.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The primary driver of warming temperatures is the buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Governments, industries, and individuals must prioritize reducing emissions by transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing stricter regulations on fossil fuels, and promoting energy efficiency. International agreements like the Paris Climate Accord are critical frameworks for encouraging countries to work together toward these goals.
Protecting Polar Ecosystems
Protecting Antarctica itself is another crucial step. Strengthening international policies like the Antarctic Treaty can help limit human activity that contributes to further environmental degradation. Ensuring that research and tourism activities adhere to strict guidelines can reduce the risk of introducing non-native species or pollutants to the region.
Advancing Climate Research
Continued research into Antarctica’s changing environment is essential for developing effective solutions. Scientists must monitor the spread of algae and moss, the melting of ice sheets, and the broader impacts on global systems. Funding and supporting climate research initiatives can provide the data needed to predict future changes and create targeted mitigation strategies.
Individual Actions Add Up
While systemic changes are vital, individuals can contribute by reducing their own carbon footprints. Simple actions like conserving energy, reducing waste, and advocating for climate policies in their communities can create a ripple effect. Supporting organizations and initiatives dedicated to climate action can also amplify individual efforts.
Though the greening of Antarctica highlights the severity of climate change, it’s not too late to act. Every step taken to reduce emissions, protect fragile ecosystems, and support research brings us closer to slowing the pace of this transformation—and safeguarding the planet for future generations.
A Sobering Signal From the South
The unexpected greening of Antarctica is more than just a curious ecological anomaly—it’s a glaring warning about the rapid pace of climate change and the fragility of our planet’s ecosystems. From the darkening effects of algae growth accelerating ice melt to the broader implications for sea levels and global weather patterns, this transformation underscores how interconnected the planet truly is.
Antarctica, often considered one of the last untouched frontiers, is now a stark reflection of humanity’s impact on the environment. The changes happening on this frozen continent serve as a reminder that no place on Earth is immune to the effects of global warming. As scientists continue to map and study this phenomenon, their findings are not just data points—they are calls to action for every individual, government, and organization.
The future of Antarctica’s landscape—and by extension, our planet—depends on the choices we make today. Whether it’s reducing emissions, advancing climate research, or taking personal steps to live more sustainably, every action counts. The time to act is now, before the green patches on the Antarctic map become a symbol of irreversible change.
Health
In A World First, A Woman’s Stem Cells Were Used To Reverse Her Type 1 Diabetes.

Imagine a life where your body’s internal “battery” runs low every single day, demanding constant recharging just to keep going. For millions of people living with Type 1 diabetes, this is the exhausting reality—one where insulin injections act as the lifeline, replacing what the body can no longer produce on its own. But what if the body could be taught to recharge itself again?
In a world-first medical breakthrough, this question has moved from possibility to reality. A woman’s own stem cells have been successfully used to reverse her Type 1 diabetes, a condition once thought to be irreversible. Scientists turned her blood stem cells into insulin-producing powerhouses, effectively “rebooting” her pancreas and allowing her body to produce insulin naturally for the first time in years.
This achievement isn’t just a milestone for one patient; it’s a bold step toward a future where Type 1 diabetes may no longer require a lifetime of management. So, how did this groundbreaking transformation happen? And what does it mean for millions waiting for a cure?
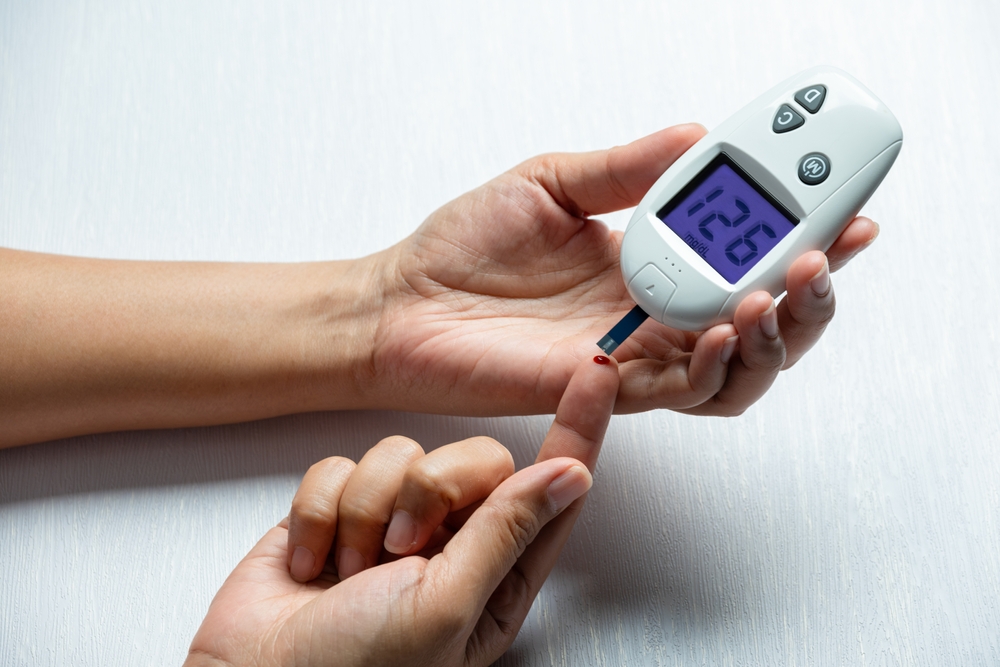
What Makes Type 1 Diabetes So Challenging?
At its core, Type 1 diabetes is a case of mistaken identity. The body’s immune system, designed to protect against harmful invaders, turns against its own insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Without insulin—a hormone that regulates blood sugar—cells are starved of energy, and blood glucose levels spiral out of control.
Unlike Type 2 diabetes, which is often linked to lifestyle and develops gradually, Type 1 diabetes strikes suddenly, typically during childhood or adolescence. There’s no prevention, no cure—only relentless management. Patients rely on a constant cycle of blood sugar monitoring, insulin injections, and dietary vigilance to stay alive. Even with diligent care, complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart problems loom over the horizon.
For those living with the condition, life becomes a balancing act. Miss a dose of insulin or miscalculate a meal, and blood sugar levels can swing dangerously, leading to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. As a result, many patients live under the weight of uncertainty, tethered to treatments that sustain life but don’t restore it.
This is what makes the recent stem cell breakthrough so revolutionary. It challenges the very permanence of Type 1 diabetes and offers a glimpse of a future where the body can once again heal itself. But how did scientists achieve what was once thought impossible? The answer lies in the incredible potential of stem cells.
The Stem Cell Breakthrough: How It Happened
For decades, scientists have searched for ways to restore insulin production in people with Type 1 diabetes. The solution has always seemed tantalizingly close, yet elusive—until now. In a world-first achievement, researchers successfully used a woman’s own blood stem cells to reverse her condition, marking a groundbreaking moment in regenerative medicine. The process was as remarkable as it was intricate. Scientists began by harvesting the woman’s hematopoietic stem cells—the versatile cells found in blood that have the ability to develop into different types of cells.
Using advanced laboratory techniques, they coaxed these stem cells to transform into insulin-producing beta cells, the very cells destroyed by the immune system in Type 1 diabetes. Once ready, these lab-grown beta cells were transplanted back into her body. What followed was nothing short of extraordinary. The cells integrated seamlessly into her pancreas and began producing insulin naturally, reducing her dependence on injections. For the first time in years, her body could regulate its blood sugar levels on its own. Unlike previous attempts that relied on donor cells—requiring recipients to take lifelong immunosuppressive drugs—this approach used the patient’s own stem cells. This eliminated the risk of rejection and represented a significant leap toward safer, personalized therapies.
The success of this procedure has not only changed one woman’s life but has opened up a new frontier in diabetes treatment. But what makes this discovery truly revolutionary? To answer that, it’s essential to understand the science and innovation that brought it to life.
Why This Discovery is Revolutionary
What sets this breakthrough apart is its unprecedented ability to address the root cause of Type 1 diabetes. For decades, treatments have focused on managing symptoms—insulin injections to replace what the body can no longer produce. But this approach, while life-sustaining, is far from perfect. Insulin therapy doesn’t stop the long-term risks of complications like nerve damage, kidney failure, or cardiovascular disease.
This discovery flips the script entirely. By converting the woman’s own stem cells into functioning insulin-producing beta cells, scientists have demonstrated a way to restore the body’s natural ability to produce insulin. Unlike previous experimental treatments that relied on donor cells—requiring lifelong immunosuppressants to prevent rejection—this technique uses autologous stem cells (cells from the patient’s own body). This means no immune rejection, no additional medications, and a much higher chance of success.
In earlier trials, researchers were able to grow beta cells in the lab, but the cells often failed to integrate properly or function consistently when transplanted. This latest achievement shows not only that beta cells can be engineered but that they can survive, adapt, and function naturally within the body. It marks the first real step toward reversing Type 1 diabetes rather than simply managing it.
For millions of people living with this condition, the implications are staggering. The success of this case suggests that personalized stem cell therapies could one day replace insulin injections altogether. It also signals a new era in regenerative medicine, where the body’s own resources can be harnessed to repair damage once considered permanent.
The Science Behind the Solution
At the heart of this groundbreaking achievement lies the extraordinary potential of stem cells—nature’s ultimate building blocks. Stem cells are unique because they can develop into almost any type of cell in the body, offering scientists a powerful tool to repair tissues and restore lost functions.
- Harvesting the Stem Cells
The process began with extracting the woman’s hematopoietic stem cells—a type of adult stem cell found in blood and bone marrow. These cells are typically responsible for generating blood cells, but researchers found a way to “reprogram” them for an entirely different purpose. - The Transformation into Beta Cells
Using advanced laboratory techniques, scientists guided the stem cells to differentiate into insulin-producing beta cells, the same cells destroyed in people with Type 1 diabetes. This process mimics natural development but takes place in a controlled lab environment. - Transplanting the Beta Cells
Once the lab-engineered beta cells were ready, they were carefully transplanted back into the patient’s body. The goal was for the new beta cells to integrate into her pancreas, replacing the function of the destroyed cells. - A Seamless Integration
The most remarkable part of the procedure is that the transplanted beta cells began functioning naturally. They sensed blood sugar levels and produced insulin as needed, effectively “rebooting” the body’s glucose regulation system.
What made this approach particularly innovative was its use of autologous cells—stem cells derived from the patient’s own body. This significantly reduced the risk of immune system rejection, a common challenge in organ or cell transplants. Unlike donor cells, which require patients to take lifelong immunosuppressive drugs, these beta cells were accepted by the body seamlessly.
What Does This Mean for the Future of Diabetes Treatment?
This groundbreaking success represents far more than a single achievement—it signals the dawn of a new era in diabetes treatment. For the first time, scientists have demonstrated that the body’s insulin production can be restored, not just supplemented.
For millions of people living with Type 1 diabetes, this could mean:
- Freedom from insulin injections: Instead of relying on daily insulin therapy, patients may one day receive a one-time stem cell treatment to restore normal pancreatic function.
- Reduced complications: By enabling the body to regulate blood sugar naturally, this approach could drastically lower the risks of long-term complications like nerve damage, kidney failure, and cardiovascular disease.
- Personalized treatment: The use of a patient’s own stem cells eliminates the need for immunosuppressive drugs, making therapies safer and more effective.
While this achievement is revolutionary, it also raises critical questions about scaling and accessibility. Stem cell therapies, while promising, are currently expensive and require advanced technology and expertise. Bringing such treatments to clinics around the world will require significant investment, rigorous testing, and regulatory approval.
A New Dawn for Diabetes
This groundbreaking achievement has redefined what once seemed impossible in the fight against Type 1 diabetes. By harnessing the power of stem cells, scientists have not only restored insulin production but also paved the way for a future where managing diabetes doesn’t mean a lifetime tethered to needles, glucose monitors, and constant uncertainty. For millions of people around the world, this success story signals hope—a glimpse of life beyond insulin therapy, where the body’s ability to heal itself can be unlocked.
However, this remarkable breakthrough is just the beginning. Challenges like scaling the procedure, ensuring long-term safety, and making the treatment accessible to all still lie ahead. Yet, the significance of this milestone cannot be understated: it proves that reversing Type 1 diabetes is not only achievable but now within our reach. For the scientific community, patients, and their families, this is not just a medical victory; it’s the first step toward a future where diabetes no longer controls lives. The dawn of a new era has begun, and with continued research and innovation, the possibilities are boundless.
Sources:
- Silva, I. B. B., Kimura, C. H., Colantoni, V. P., & Sogayar, M. C. (2022). Stem cells differentiation into insulin-producing cells (IPCs): recent advances and current challenges. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02977-y
- – A new therapy for treating Type 1 diabetes. (n.d.). Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). https://hsci.harvard.edu/news/new-therapy-treating-type-1-diabetes
News
Woman, Who Got Pregnant During Nine-Year Affair With Jay-Z, Breaks Her Silence

Carmen Bryan, a name that has become synonymous with some of hip-hop’s most infamous dramas, has resurfaced in the spotlight with bold new revelations. Known for her turbulent nine-year affair with Jay-Z while dating rap legend Nas, Bryan has long been a central figure in one of music’s most storied rivalries. Recently, she broke her silence on allegations surrounding Jay-Z, sparking intense public interest and reigniting discussions about her controversial past. What did she say, and how does it tie into the broader narrative of her life entangled with hip-hop’s elite?

Image credits: Instagram @carmenbryan
Carmen Bryan’s Memoir and Legacy
In 2006, Carmen Bryan published her memoir, It’s No Secret: From Nas to Jay-Z, from Seduction to Scandal—a Hip-Hop Helen of Troy Tells All, offering an insider’s perspective on the complexities of the hip-hop world. Drawing from her experiences working at Def Jam and Capitol Records, and her relationships with prominent artists, Bryan provides a candid narrative of her life intertwined with hip-hop culture.
In her memoir, Bryan reflects on her relationships, including the affair with Jay-Z, and the resulting tensions within the hip-hop community. She recalls the moment she lost respect for Jay-Z after he released the track “Supa Ugly,” stating: “Wrong move! That was the moment I lost all respect for SC [Shawn Carter].”
Bryan’s memoir has been described as “an exclusive behind-the-scenes look at life in the rap world,” shedding light on the personal dynamics that influenced some of the most significant feuds in hip-hop history.
Beyond her memoir, Bryan’s legacy is marked by her willingness to speak openly about her experiences, challenging the often glamorized portrayal of the hip-hop lifestyle. Her narrative contributes to a broader understanding of the personal sacrifices and moral dilemmas faced by those within the industry.
The Affair and Its Impact
Carmen Bryan’s clandestine relationship with Jay-Z, spanning from 1995 to 2004, unfolded concurrently with her involvement with rapper Nas, the father of her daughter, Destiny. This intricate love triangle not only intensified the personal dynamics among the trio but also ignited one of hip-hop’s most notorious feuds.
The rivalry between Nas and Jay-Z, fueled by personal grievances, became a public spectacle through their music. Jay-Z’s track “Supa Ugly” included explicit references to his affair with Bryan, rapping about intimate encounters in a Jeep and leaving used condoms in her daughter’s baby seat. Bryan expressed her disgust, stating, “Wrong move! That was the moment I lost all respect for SC [Shawn Carter].”
Bryan’s pregnancy during the affair, which ended in miscarriage, added another layer of complexity to the situation. She revealed that the pregnancy was unplanned and that she informed Jay-Z only after the miscarriage had occurred. This revelation, along with the public airing of their affair, contributed to the deterioration of her relationship with Nas and intensified the feud between the two rappers.
The public nature of these relationships and the ensuing feud had a significant impact on the hip-hop community and its audience. Studies have shown that celebrity scandals can influence public perception and shape societal narratives. Media coverage of such events often leads to the establishment or dismantling of stereotypes and can affect consumer behavior and attitudes toward the celebrities involved.
In the case of Bryan, Nas, and Jay-Z, the public feud not only affected their personal lives but also had professional implications. The rivalry brought increased attention to their music, with fans and critics analyzing lyrics for references to the affair. This scrutiny contributed to the commercialization of their personal conflicts, blurring the lines between their private lives and public personas.
Bryan’s memoir, “It’s No Secret: From Nas to Jay-Z, from Seduction to Scandal—a Hip-Hop Helen of Troy Tells All,” offers an insider’s perspective on these events. In the book, she provides candid accounts of her relationships with both rappers, shedding light on the personal and professional challenges she faced. Her story underscores the complexities of navigating love and loyalty within the high-stakes world of hip-hop.
The affair and its aftermath highlight the intricate interplay between personal relationships and public image in the entertainment industry. For Bryan, the experience was transformative, leading her to reflect on her choices and their consequences. As she stated, “I still love SC [Jay-Z/Shawn Carter], and I still love Nas. Love is an energy that can never be destroyed.”
Carmen Bryan’s Criticism of Jay-Z

Image credits: Instagram @carmenbryan
Carmen Bryan, known for her past relationships with prominent figures in the hip-hop industry, has recently voiced criticism of Jay-Z following serious allegations against him. In light of these events, Bryan took to Instagram to express her views, stating: “These days people don’t defend what is right, they defend who they like! And that’s why we call you ‘groupie’.”
Bryan also referenced Jay-Z’s lyrics from Kanye West’s track “Monster,” highlighting the lines: “Kill a block, I murder the avenues, I rape and pillage your village, women and children.”
This is not the first time Bryan has been vocal about her disapproval of Jay-Z’s actions. In her memoir, “It’s No Secret,” she discusses her reaction to Jay-Z’s song “Supa Ugly,” which contained explicit references to their affair. Bryan expressed her disgust, stating: “Wrong move! That was the moment I lost all respect for SC [Shawn Carter].”
Jay-Z’s Legal Battle
In December 2024, Jay-Z, born Shawn Carter, faced a civil lawsuit accusing him and Sean “Diddy” Combs of raping a 13-year-old girl at an after-party following the 2000 MTV Video Music Awards. The plaintiff, identified as “Jane Doe,” alleged that both men assaulted her at a New York City event.
Jay-Z vehemently denied the allegations, describing them as a “blackmail attempt.” He expressed concern for his family, stating, “My wife and I will have to sit our children down… and explain the cruelty and greed of people.”
The lawsuit’s credibility came into question when the accuser admitted to inconsistencies in her account, including misidentifying individuals and events. Despite these discrepancies, she maintained that the assaults occurred.
In response, Jay-Z’s legal team filed a motion to dismiss the case, citing the inconsistencies and lack of evidence. They also requested that the accuser’s identity be revealed, arguing that anonymity hindered a fair defense.
This legal battle underscores the complexities of high-profile cases, where public perception and media coverage can significantly impact proceedings. Studies indicate that media portrayal of such cases can influence public opinion and potentially affect judicial outcomes.
The Legacy of Controversy and Accountability
The allegations against Jay-Z and the subsequent reactions from Carmen Bryan and the public have brought new attention to the complexities of fame, accountability, and personal relationships within the entertainment industry. The accusations and the legal battle have cast a shadow over Jay-Z’s illustrious career, raising questions about how society navigates the intersection of art, morality, and justice.
For Carmen Bryan, this moment has reignited interest in her past, but it also speaks to her enduring narrative of speaking her truth, regardless of the cost. As she noted in her memoir, “Love is an energy that can never be destroyed,” underscoring the lasting emotional impact of her relationships with Jay-Z and Nas.
Meanwhile, the public remains divided, reflecting the broader cultural struggle to reconcile admiration for talented figures with the scrutiny of their personal actions. The case serves as a reminder of the importance of fair investigations, the risks of trial by public opinion, and the ethical challenges that come with holding influential figures accountable.
Featured image from Instagram @carmenbryan
News
We Regret To Inform You The Pool Drain/Intestines Thing Is Not An Urban Legend

Have you ever dismissed a chilling story, brushing it off as an urban legend? Like the warnings whispered about the dangers of sitting on pool drains—surely too bizarre to be true. But what if the nightmare isn’t a myth? What if it’s horrifyingly real?
The physics of pool drains can turn an everyday swim into a catastrophic event. A force so strong it could eviscerate a human body. It sounds impossible—something plucked from the pages of horror fiction—but verified cases tell a much darker story. This isn’t just a cautionary tale; it’s a wake-up call.
For example, the tragic case of six-year-old Valerie Lakey highlights just how devastating these accidents can be. “Valerie’s injuries were severe,” explains the official report, “she lost 80% of her intestines.” These words alone carry the weight of an unimaginable reality—one that demands attention.

The Gruesome Reality: What Really Happens
The idea of a pool drain causing catastrophic injuries may sound like a plot twist in a horror movie, but it’s a grim reality backed by documented cases. Pool drains operate with powerful suction, designed to circulate water effectively. However, when something—or someone—gets too close to an uncovered or malfunctioning drain, the force can become deadly.
One of the most haunting examples is Valerie Lakey, a six-year-old whose life was permanently altered during a seemingly innocent day at the pool. As noted in reports, Valerie was sitting near a pool drain when the suction force pulled her intestines through her rectum. Doctors later revealed that she had lost 80% of her intestines. This devastating injury required extensive surgeries and lifelong medical care, leaving an indelible mark not just on Valerie but also on the conversation around pool safety.
It’s not just children who are at risk. Adults have also experienced entrapment injuries, with incidents ranging from limb fractures to fatal drownings when they couldn’t escape the suction. What’s even more alarming is how quickly these accidents happen—often in a matter of seconds, leaving little time for intervention.
The gruesome reality is that pool drain accidents, though rare, are entirely preventable with the right safety measures in place. But understanding how these tragedies occur is the first step toward ensuring they don’t happen again.
How Pool Drain Accidents Happen
At first glance, a pool drain seems harmless—just another fixture keeping the water clean and circulating. But behind its innocuous appearance lies a dangerous force. Pool drains work by pulling water through the filtration system, creating suction that can become extremely powerful if a drain cover is missing, damaged, or improperly installed.
The danger escalates when a body part or clothing comes into contact with the drain. The suction creates a vacuum-like seal, making it nearly impossible to break free. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has reported that the suction from a pool drain can generate hundreds of pounds of force, enough to trap even a fully grown adult underwater.
Children are particularly vulnerable due to their smaller size. Incidents often involve entrapment of hair, limbs, or clothing, but the most harrowing cases are when suction leads to evisceration, as in the tragic story of Valerie Lakey. In some instances, victims have also suffered broken bones or joint dislocations while trying to escape the pull of the drain.
The risk is heightened in older pools that may not meet modern safety standards. A missing or broken drain cover, a single-drain system, or improper maintenance can all create the perfect conditions for a disaster. And because pool drain dangers aren’t commonly discussed, many swimmers and parents remain unaware of the risks.
The Aftermath: Physical and Emotional Toll
Surviving a pool drain accident often leaves victims with injuries that are as life-altering as they are unimaginable. For Valerie Lakey, the aftermath of her accident required extensive medical intervention. As reported, “Valerie was left with permanent injuries that would require ongoing care for the rest of her life.” The physical toll alone—losing the majority of her intestines—was catastrophic.
Beyond the physical scars, the emotional burden is equally profound. Survivors often deal with long-term trauma, including anxiety around water and the psychological impact of their injuries. Families, too, are left grappling with the emotional strain and the financial costs of medical care and rehabilitation.
In many cases, these incidents have prompted victims’ families to take legal action. For example, Valerie’s family pursued a landmark lawsuit, which resulted in a $25 million settlement against the pool’s manufacturers and operators. The case not only highlighted the devastating consequences of negligence but also served as a catalyst for significant changes in pool safety regulations.
These tragedies illustrate that the consequences of pool drain accidents extend far beyond the initial incident. They are a stark reminder of why safety measures and regulations are not just necessary—they’re critical for preventing such life-changing events.
Regulations and Safety Measures: What’s Been Done
In the wake of harrowing incidents like Valerie Lakey’s, lawmakers and safety advocates have pushed for stricter pool safety regulations to prevent future tragedies. One of the most significant outcomes was the passage of the Virginia Graeme Baker Pool and Spa Safety Act (VGB Act) in 2007. This federal law, named after a young girl who drowned due to drain entrapment, mandates safety measures for public pools and spas across the United States.
The VGB Act requires the use of anti-entrapment drain covers, which are designed to prevent suction accidents by diffusing the force of the drain. Additionally, it mandates dual-drain systems in new pools, which help minimize suction by spreading the force across multiple outlets. These measures are crucial in reducing the risk of entrapment injuries or deaths.
While these regulations have undoubtedly saved lives, enforcement remains a challenge. Public pools are subject to inspections, but private pools often fall outside the scope of these requirements. Moreover, older pools may not comply with modern standards unless retrofitted with updated safety features.
Despite these advancements, some advocates argue that more needs to be done. As one safety expert notes in the IFLScience article, “These tragedies are entirely preventable, but only if we’re vigilant about enforcing and adhering to safety standards.” This sentiment underscores the importance of continued education and compliance to ensure every pool, public or private, is a safe space for swimmers.
The fight for safer pools isn’t over. Raising awareness about these regulations and encouraging pool owners to take proactive steps could help eliminate preventable accidents and their devastating consequences.
Preventing Tragedy: How to Stay Safe
Understanding the dangers of pool drains is the first step toward prevention. While regulations like the VGB Act have introduced life-saving measures, individual responsibility is key to ensuring every swim is a safe one. Whether you’re a pool owner or a frequent swimmer, here are some practical steps to protect yourself and others:
- Inspect Pool Drains Regularly
Always check that pool drain covers are intact and meet modern safety standards. A broken or missing cover is a red flag that should never be ignored. - Teach Children Pool Safety
Explain to kids why they should avoid sitting or playing near pool drains. Simple rules, like “stay away from the drain,” can make a big difference. - Supervise Closely
Drowning and entrapment can happen in seconds, especially with children. Active supervision during swim time is critical to prevent accidents. - Upgrade Older Pools
If you own a pool, ensure it complies with safety regulations, including the use of anti-entrapment covers and dual-drain systems. Professional inspections can help identify risks. - Know Emergency Protocols
Learn how to shut off the pool’s suction system in an emergency and ensure you have quick access to emergency contacts.
By taking these steps, pool users and owners alike can reduce the risks associated with dangerous suction forces. Pool safety isn’t just a matter of legislation; it’s a collective effort that starts with awareness and action.
Addressing the Myths: Why This Isn’t Just a Scary Story
The idea of pool drains causing catastrophic injuries is so unsettling that many people dismiss it as an urban legend. This misconception leads to complacency, which is why it’s essential to confront the uncomfortable truth head-on.
As we have highlight the importance of education, stating, “This isn’t an exaggeration or scare tactic—these accidents are rare but very real.” By perpetuating myths or downplaying their severity, we fail to prepare ourselves and our loved ones for the potential dangers.
Misinformation can lead to negligence, whether it’s ignoring a missing drain cover or assuming that these accidents are too rare to worry about. The truth is, awareness saves lives. Sharing accurate information and acknowledging these tragedies as preventable can make pools safer for everyone.
It’s time to replace myths with facts. Understanding the reality of pool drain accidents isn’t about fear—it’s about equipping people with the knowledge to protect themselves and others.
Animals
US Cruise Line To Launch Dog-Friendly Cruise In November 2025

Imagine setting sail on a luxurious cruise where your four-legged best friend is not only welcome but celebrated. For years, pet owners have faced a tough choice when planning vacations: leave their beloved dogs behind or forgo the trip altogether. Now, that dilemma is about to change. A US cruise line has announced plans for a groundbreaking dog-friendly voyage in 2025, promising an experience unlike anything seen before on the high seas.
With exclusive amenities, exciting activities, and a few surprising rules, this innovative cruise aims to redefine travel for dog lovers. But what makes this sailing truly unique, and how exactly will it work?
The Vision Behind the Cruise
This initiative is driven by a deep-seated desire to integrate pets into the travel experiences of their owners, acknowledging the significant role that dogs play as family members.
Steve Matzke, the visionary behind Cruise Tails, encapsulated this sentiment, stating, “I consider my Yorkie, Louis, to be part of my family, and for years I missed out on the ‘family reunion’ cruise because I will not travel without him. I want to change that for myself and other dog lovers.”
This pioneering venture not only caters to the emotional bonds between pet owners and their dogs but also taps into a burgeoning market of travelers seeking pet-inclusive vacations.
By offering specialized amenities and activities tailored for canine companions, the cruise aims to set a new standard in the travel industry, where pets are not just allowed but celebrated as integral participants in the journey.
The overwhelming response to this announcement underscores the demand for such experiences, with thousands expressing interest in participating.
As Matzke noted, “The enthusiasm and positive response we’ve received so far have been incredible. We’re thrilled to be able to provide such a unique travel experience where dogs are not just allowed, but celebrated as part of the family.”

Onboard Amenities for Dogs
On the world’s first dog-friendly cruise, organized by Cruise Tails and Expedia Cruises of West Orlando, offers an array of amenities tailored to ensure a comfortable and enjoyable experience for canine passengers and their owners.
Each pet-friendly stateroom is equipped with a private relief station on the balcony, maintained by an assigned “Pet Butler” dedicated to the cleanliness and comfort of both the dog and its human companions.
To maintain a harmonious environment, dogs are required to stay in designated pet-friendly areas and are not permitted in specific zones such as restaurants, the casino, pool decks, and the spa.
This innovative approach to cruising reflects a growing trend among pet owners seeking inclusive vacation experiences.
A survey by the American Pet Products Association found that 37% of pet owners travel with their pets every year, a significant increase over past decades.
By offering specialized amenities and services, this cruise aims to set a new standard in pet-friendly travel, ensuring that both dogs and their owners can enjoy a memorable journey together.
The Cruise Experience
Embarking on this unprecedented voyage, both canine companions and their human counterparts can anticipate a plethora of engaging activities and amenities designed to ensure a memorable journey.
Pet-Centric Activities
- Costume Contests and Parades: Showcase your dog’s unique style in themed events that promise entertainment and camaraderie among guests.
- Dog Shows and Training Sessions: Participate in exhibitions and receive expert training advice to enhance your pet’s skills and behavior.
- Grooming Services and Puppy Massages: Pamper your pooch with professional grooming and relaxing massages, ensuring they feel as rejuvenated as you do.
- Splash Stations: Let your dog cool off and play in designated water areas tailored for safe canine enjoyment.
Human-Centric Amenities
While the cruise is tailored for dogs, human passengers are not left out. The ship boasts a variety of facilities, including:
- Dining Venues: Twelve chef-crafted, island-inspired dining options to satisfy diverse culinary preferences.
- Entertainment and Lounges: Thirteen action-packed lounges offering live entertainment and music for relaxation and enjoyment.
- Spa and Casino: Access to the St. Somewhere Spa & Salon for rejuvenation, and the Margaritaville Casino for those feeling lucky.
To maintain a harmonious environment onboard:
- Pet Butlers: Each family with a dog will be assigned a “Pet Butler” dedicated to maintaining cleanliness and attending to the pet’s needs throughout the voyage.
- Private Relief Stations: Staterooms accommodating dogs will feature private relief areas on balconies, ensuring convenience for pet needs.
- Designated Pet Areas: While dogs are welcome in many parts of the ship, certain areas such as restaurants, the casino, pool decks, and the spa are off-limits to maintain hygiene and comfort for all guests.
Steve Matzke of Cruise Tails shared his personal motivation behind the initiative: “I consider my Yorkie, Louis, to be part of my family, and for years I missed out on the ‘family reunion’ cruise because I will not travel without him. I want to change that for myself and other dog lovers.”

How to Join the Cruise
The world’s first dog-friendly cruise requires careful preparation to ensure a seamless experience for both you and your canine companion.
Application Process
Applications are now open for this exclusive voyage, with only 250 spots available for dogs. Interested pet owners should promptly submit their applications through the official Cruise Tails website.
Health and Vaccination Requirements
To ensure the well-being of all passengers, canine participants must be fully vaccinated and accompanied by a health certificate signed by a licensed veterinarian. This protocol is essential for maintaining a healthy environment onboard.
Pet Butler Service
Each dog-owning family will be assigned a “Pet Butler” to maintain cleanliness and comfort during the trip, ensuring a pleasant experience for all guests.
Designated Pet Areas
While dogs are welcome in many areas of the ship, certain zones such as restaurants, the casino, pool decks, and the spa are off-limits to maintain hygiene and comfort for all guests.
Booking Information
Reservations for the cruise began in December 2024. Given the limited availability and high demand, interested parties are encouraged to secure their spots promptly.
Challenges and Concerns
While the upcoming dog-friendly cruise by Margaritaville at Sea has generated significant excitement among pet owners, it has also sparked a range of concerns and criticisms from various quarters.
- Hygiene and Allergies: A primary concern revolves around maintaining cleanliness on board. With up to 250 dogs, ensuring sanitary conditions in shared spaces poses a considerable challenge. Potential issues include pet hair, odors, and the possibility of accidents in public areas, which could affect passengers with allergies or sensitivities.
- Safety and Behavior: The dynamics of having numerous dogs in a confined environment raise questions about safety. Unfamiliar surroundings and the presence of other animals might lead to unpredictable behavior, including aggression or anxiety-induced reactions. Ensuring that all canine passengers are well-behaved and that owners can effectively manage their pets is crucial to prevent incidents.
- Limited Options for Non-Dog Lovers: Some travelers express concerns that the introduction of pet-friendly cruises may reduce the availability of dog-free vacation options. They fear that if such cruises become popular, it could lead to a decrease in choices for those who prefer or require pet-free environments due to allergies, phobias, or personal preferences.
- Logistical Challenges: Accommodating a large number of dogs necessitates significant logistical planning. This includes creating adequate potty areas, ensuring the availability of veterinary care, and managing the additional staff required to cater to canine needs. Skeptics question whether the cruise line can effectively address these complexities without compromising the overall experience for all passengers.
- Impact on Cruise Experience: Traditional cruisers worry that the presence of numerous dogs might alter the ambiance of the voyage, potentially making it less relaxing and more chaotic. Concerns include noise from barking, disruptions in common areas, and the overall shift from the luxury experience they anticipate.
In response to these concerns, the organizers have implemented measures such as assigning “Pet Butlers” to maintain cleanliness and designating specific pet-friendly areas to mitigate potential issues. However, the success of this pioneering venture will largely depend on the effective execution of these strategies and the cooperation of all participants.
Paws at Sea: A New Era in Travel
The dog-friendly cruise by Margaritaville at Sea is more than just a novelty—it’s a bold reimagining of travel for pet lovers. With tailored amenities, engaging activities, and innovative solutions for practical concerns, this voyage offers an unparalleled opportunity for pet owners to share an unforgettable experience with their four-legged companions. While logistical challenges remain, the overwhelming excitement from travelers and pet enthusiasts alike indicates this initiative has the potential to redefine cruising for a new, pet-inclusive era.
As the waitlist opens and final preparations unfold, one question lingers: could this be the beginning of a new wave of pet-friendly travel? If this first voyage succeeds, the dream of setting sail with your loyal companion may soon become an annual tradition.
Awareness
Marathon runner diagnosed with terminal cancer urges people not to dismiss small symptom he experienced

When Lee Rawlinson, a 51-year-old marathon runner and devoted father, began experiencing a minor discomfort in his stomach, he brushed it off as nothing serious. After all, how could something so small disrupt the life of someone so strong and active? But that seemingly harmless symptom turned out to be a warning sign of something far more devastating.
Now, as Lee faces an unimaginable reality, he’s sharing his story with one urgent message: don’t ignore your body’s signals—no matter how insignificant they seem. His journey is a powerful reminder that sometimes, the smallest symptoms can hide the biggest truths.
The Symptom That Was Easy to Overlook
In January, Lee Rawlinson began experiencing a persistent dull ache in his lower abdomen. As a seasoned marathon runner, he attributed this discomfort to stress or perhaps his rigorous training regimen. “I just thought it was stress-related,” Lee admitted.
However, by September, the pain had intensified to an unbearable degree. “I was taking painkillers every day, and co-codamol, and it wasn’t touching the sides,” he recalled. “If you can imagine a scaffolding pole and someone slowly pushing it through you, right through to your back, it was like that.”
This escalation led Lee to seek emergency medical attention, where he received the devastating diagnosis of terminal pancreatic cancer. The cancer had already spread to his liver, making it inoperable and leaving him with only months to live.
Lee’s experience underscores a critical issue: the early symptoms of pancreatic cancer are often subtle and easily dismissed. According to the Mayo Clinic, pancreatic cancer often doesn’t cause symptoms until the disease is advanced. When they do occur, signs and symptoms may include abdominal pain that radiates to the back, loss of appetite, weight loss, jaundice, light-colored stools, and dark-colored urine.
A study published by the American Cancer Society highlights the challenges in early detection, noting that pancreatic cancer is hard to find early. The pancreas is deep inside the body, so early tumors can’t be seen or felt during routine physical exams. People usually have no symptoms until the cancer has become very large or has already spread to other organs.
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. The pancreas, located behind the stomach, plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. This type of cancer is particularly aggressive and often goes undetected until it has reached an advanced stage.
Types of Pancreatic Cancer
There are two primary types of pancreatic cancer:
- Exocrine Tumors: The most common form, accounting for about 95% of cases. These tumors affect the exocrine glands responsible for producing digestive enzymes.
- Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs): Less common, these tumors develop in the endocrine cells that produce hormones like insulin. NETs tend to have a better prognosis compared to exocrine tumors.
Pancreatic cancer is often dubbed the “silent killer” because its early symptoms are subtle and easily overlooked. Common signs include:
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back. Lee Rawlinson described his pain as feeling like “a scaffolding pole and someone slowly pushing it through you, right through to your back.”
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without changes in diet or exercise.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, often without accompanying pain.
- Digestive Issues: Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and changes in stool.
These symptoms are often mistaken for less severe conditions, leading to delays in diagnosis. According to Cancer Research UK, pancreatic cancer is the 10th most common cancer in the UK, with around 10,500 people diagnosed each year. However, it is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths, underscoring its severity.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer:
- Age: More than 45% of cases are diagnosed in individuals aged 75 and over.
- Smoking: Tobacco use significantly elevates risk.
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Long-term inflammation of the pancreas.
- Family History: A history of pancreatic cancer in close relatives.
- Obesity: Excess body weight has been linked to a higher incidence of pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic cancer has one of the lowest survival rates among major cancers. The five-year survival rate is approximately 7-9%, largely due to late-stage diagnoses. Early detection is critical but challenging, emphasizing the importance of awareness and prompt medical attention for persistent, unexplained symptoms.
Lee’s Message: Don’t Ignore Small Signs

Image Credits: Instagram @rawly2010
Lee Rawlinson’s journey from experiencing a minor abdominal ache to facing terminal pancreatic cancer serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of heeding our body’s signals, no matter how insignificant they may seem. Initially dismissing his discomfort as stress-related, Lee now reflects on the consequences of overlooking such symptoms.
“I just thought it was stress-related,” Lee admitted, recalling the dull ache that began in January. By September, the pain had intensified to an unbearable degree, leading to his diagnosis on Halloween. “If you can imagine a scaffolding pole and someone slowly pushing it through you, right through to your back, it was like that,” he described.
Lee’s experience underscores a critical issue: the early symptoms of pancreatic cancer are often subtle and easily dismissed. According to Cancer Research UK, pancreatic cancer is the 10th most common cancer in the UK, with around 10,500 people diagnosed each year. However, it is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths, underscoring its severity.
Lee’s story serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of paying attention to persistent, u, no matter how minor they may seem. Early detection is crucial in improving outcomes for pancreatic cancer, a disease that remains one of the deadliest forms of cancer.
In light of his experience, Lee urges others to be vigilant and proactive about their health. le to sit up and listen and think, what can we do for this not to destroy another young family’s life?” he emphasized.
His message is clear:
- Listen to Your Body: Don’t dismiss persistent symptoms as trivial.
- Seek Medical Advice: Consult healthcare professionals when something feels off.
- Advocate for Early Detection: Early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
By sharing his story, Lee hopes to raise awareness about the subtle signs of pancreatic cancer and encourage others to take prompt action, potentially saving lives and preventing other families from facing similar heartbreak.
Making the Most of Time Left
Facing a terminal diagnosis, Lee Rawlinson is channeling his energy into creating cherished memories with his family. Determined to make his remaining time meaningful, he has planned special experiences for his wife, Faye, and their children, Darcey and Marley.
One of the family’s most anticipated adventures is a trip to Lapland. Lee shared his excitement: “The kids have never been on a plane before, so they’re going to fly for the first time and look out the window and see snow, and I’m going to see their reaction. It’s going to be amazing.”
In addition to the Lapland trip, the family has received VIP tickets to an Arsenal football match, allowing them to share in one of Lee’s passions. These experiences are not just about the activities themselves but about the lasting memories they will create together.
Lee’s focus on family time aligns with research highlighting the importance of quality of life for terminally ill patients. Studies have shown that engaging in meaningful activities and spending time with loved ones can significantly enhance emotional well-being during end-of-life care.
Despite the challenges, Lee remains resolute in his mission to raise awareness about pancreatic cancer. He hopes that by sharing his story, others will be prompted to seek medical advice for unusual symptoms, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses and better outcomes. “I want to get people to sit up and listen and think, what can we do for this not to destroy another young family’s life?” he emphasized.
Raising Awareness for Change
Confronted with a terminal diagnosis, Lee Rawlinson has transformed his personal battle into a mission to raise awareness about pancreatic cancer. He emphasizes the critical need for early detection and advocates for increased research funding to combat this aggressive disease.
“Survival for pancreatic cancer has barely improved since the 1970s, and it’s got to change,” Lee stated. “I want to get people to sit up and listen and think, what can we do for this not to destroy another young family’s life?”
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the deadliest cancers, with a five-year survival rate of only 11%.
This high mortality rate is largely due to late-stage diagnoses, as early symptoms are often subtle and overlooked.
Efforts to improve early detection are underway. For instance, the Early Diagnosis Research Alliance, established in 2018, brings together experts aiming to develop new tools for the early detection of pancreatic cancer.
Additionally, the Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection (PRECEDE) Consortium focuses on identifying high-risk individuals and advancing early diagnosis research.
An Unforgettable Message for Us All
Lee Rawlinson’s story is one of courage, resilience, and love. Faced with terminal pancreatic cancer, Lee has chosen to use his remaining time to make lasting memories with his family while spreading a critical message: no symptom is too small to ignore.
His plea resonates deeply: “Survival for pancreatic cancer has barely improved since the 1970s, and it’s got to change. I want people to sit up and listen and think, what can we do for this not to destroy another young family’s life?” Lee’s bravery in raising awareness for this deadly disease highlights the urgent need for better research, early detection tools, and increased public understanding.
Though his time may be limited, Lee’s mission to inspire others to act on even the smallest signs of illness leaves behind a legacy of awareness and hope—a gift that could save lives.
His story serves as a reminder to listen to your body, cherish every moment, and advocate for change.
Featured image from Instagram @rawly2010
News
Proposed $20,000,000,000,000 Tunnel Would Get You From NYC To London In Just 54 Minutes

Imagine this: the Atlantic Ocean, often seen as an unyielding barrier between continents, transformed into a high-speed highway connecting New York and London in less than an hour. No turbulence, no delays, just a 54-minute journey hurtling through an underwater tunnel at nearly 4,000 mph—faster than a jetliner, rivaling the speed of sound.
This isn’t the plot of a sci-fi blockbuster but the audacious vision of engineers who dream of revolutionizing travel as we know it. With an estimated price tag of $20 trillion—roughly the combined GDP of the world’s largest economies—this proposed transatlantic tunnel promises to shrink the world in ways we’ve never imagined. But is this bold ambition a marvel of human ingenuity or an impossible feat too ambitious for our time?

What is the Transatlantic Tunnel?
The concept of a transatlantic tunnel has existed in the realm of dreams and science fiction for over a century, but recent advancements in technology are bringing it closer to the realm of possibility. At its core, the idea is both radical and deceptively simple: a submerged tube stretching 3,100 miles across the Atlantic Ocean, inside which magnetically levitated trains (maglev) would travel in a near-vacuum environment. The absence of air resistance would allow these trains to reach mind-bending speeds of up to 4,000 mph.
Magnetic levitation technology isn’t new. In fact, it’s already used in Japan’s cutting-edge Shinkansen trains, which reach speeds of over 370 mph. However, scaling this to the level required for a transatlantic tunnel presents an engineering challenge like no other. Beyond the technology, the tunnel itself would need to withstand crushing oceanic pressures, seismic activity, and potential collisions with ships or submarines.
Originally imagined in the early 1900s by futurists and popularized in science fiction, the transatlantic tunnel was long dismissed as a pipe dream. But today, a mix of technological optimism and global connectivity has reignited discussions about its feasibility. While still far from a concrete plan, the vision of seamless intercontinental travel is no longer confined to fiction—it’s inching its way toward the drawing board of real-world engineering.
The Engineering Feat of the Century
Building a tunnel across the Atlantic Ocean is no ordinary construction project—it’s a challenge that pushes the boundaries of what humanity can achieve. At over 3,100 miles long, this underwater marvel would dwarf existing infrastructure like the Channel Tunnel, which spans a mere 31 miles beneath the English Channel. The logistical, technological, and environmental hurdles are as immense as the tunnel itself.
First, consider the structural demands. The tunnel would have to endure immense pressure from the ocean depths, where water pressure can exceed 5,800 psi—strong enough to crush conventional materials. Engineers propose using a combination of lightweight yet highly durable materials, potentially carbon-fiber composites, to construct the vacuum-sealed tubes. But even with advanced materials, creating a structure this long, without sagging or collapsing under its own weight, is a monumental task.
Then there’s the issue of magnetic levitation technology. While maglev trains already exist, scaling them to reach speeds of 4,000 mph in a vacuum is uncharted territory. Maintaining the vacuum itself, free from air leaks across thousands of miles, would require unprecedented precision and reliability. Additionally, the train system would need advanced safety protocols to prevent catastrophic accidents at such high speeds, where even minor errors could have devastating consequences.
Finally, the project would require laying the tunnel on the seabed or suspending it using tension cables—a feat complicated by uneven ocean floors, tectonic activity, and extreme weather conditions. The engineering would need to account for everything from deep-sea currents to the potential for ship anchors or submarine interference. It’s not just about building a tunnel; it’s about creating a structure that can coexist with the unpredictable forces of the ocean for decades, if not centuries.

The Eye-Watering Cost and Funding Challenges
The price tag for the proposed transatlantic tunnel is almost as staggering as the project itself—a jaw-dropping $20 trillion. To put that in perspective, it’s equivalent to nearly the combined annual GDP of the United States, China, and the European Union. While the idea of such an engineering marvel is undeniably exciting, financing it is another story altogether.
As one source puts it, this project “would require the kind of resources and global cooperation on a scale that humanity has never seen before.” Unlike conventional infrastructure, which can rely on national funding or public-private partnerships, this tunnel would necessitate collaboration between multiple governments, corporations, and engineering experts across the globe.
However, many experts remain skeptical. Michael Laine, founder of LiftPort Group, stated bluntly, “The expense and difficulty of constructing it far outweigh any potential benefits.” Such criticism is echoed by economists and engineers alike, who question whether the tunnel could ever recoup its investment. Would enough people even use it to justify the astronomical cost?
Moreover, the financing dilemma goes beyond cost alone. The geopolitical implications are immense. Who would own and control such a massive piece of infrastructure spanning international waters? And how would disagreements over funding, maintenance, and profits be resolved between nations? Without ironclad agreements and unprecedented levels of cooperation, the project could falter before construction even begins.
Despite these challenges, proponents argue that the tunnel represents a step toward a more interconnected and efficient world. But with such an immense price tag and countless logistical hurdles, many are left wondering if the idea is simply too good to be true.
Time-Saving Potential and Its Global Impact
The most tantalizing aspect of the transatlantic tunnel is its promise to revolutionize travel by reducing the journey between New York City and London to just 54 minutes. Currently, a transatlantic flight takes around seven hours—a monumental difference that could reshape how people and goods move across the world.
This level of speed could redefine the concept of globalization. As CNN highlighted, such a tunnel “would make it possible to live in one city and work in the other,” creating unprecedented opportunities for international business and collaboration. Imagine attending a morning meeting in Manhattan and enjoying dinner in London on the same day, all without the fatigue of a long-haul flight.
Beyond convenience, the tunnel has the potential to drastically reduce carbon emissions. Air travel is one of the most significant contributors to global CO₂ levels, and a vacuum-based maglev train could provide a cleaner alternative. Proponents argue that if the tunnel is powered by renewable energy, it could pave the way for more sustainable intercontinental transportation.
However, critics question whether the world is ready for such a seismic shift. The aviation industry, for example, could face immense disruption, with airlines potentially losing a significant share of transatlantic traffic. Entire economies reliant on air travel could be forced to adapt. Additionally, the sheer scale of the tunnel might create new environmental challenges, such as impacts on marine ecosystems during construction.
The Critics Weigh In: Too Ambitious or Visionary?
Despite its groundbreaking allure, the proposed transatlantic tunnel has no shortage of skeptics. For many experts, the project seems more like a fantastical dream than a feasible reality. From engineering hurdles to astronomical costs, critics argue that the obstacles far outweigh the benefits.
One major concern is the sheer complexity of building and maintaining a 3,100-mile tunnel under the Atlantic Ocean. The tunnel would need to withstand the crushing pressure of the ocean while remaining completely airtight to maintain the vacuum required for maglev trains to reach speeds of 4,000 mph. Such a structure would demand engineering precision and durability on a scale humanity has never achieved—and sustained for decades.
Then there’s the risk factor. High-speed travel in a vacuum is uncharted territory, and the consequences of a catastrophic failure could be unimaginable. What happens if the vacuum system fails? How would passengers be evacuated in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean? These are critical safety questions without clear solutions.
Critics also raise concerns about geopolitical cooperation. A project of this magnitude would require unprecedented levels of collaboration and trust between nations. Coordinating construction, funding, and eventual management of a tunnel spanning international waters is no small feat, and disagreements over ownership or maintenance could jeopardize the entire endeavor.
A Bold Vision or an Impossible Dream?
The proposed transatlantic tunnel represents one of the most ambitious ideas ever conceived—a project that could redefine global connectivity, transform economies, and reshape the way we think about travel. With the ability to transport passengers from New York to London in just 54 minutes, the tunnel promises a future where oceans are no longer barriers but seamless bridges between continents.
However, the challenges are as monumental as the vision itself. From the staggering $20 trillion price tag to unprecedented engineering and geopolitical complexities, the project is a gamble that tests the limits of human innovation. Critics question whether the risks—financial, technological, and environmental—are too great, while proponents see it as a necessary leap toward a more interconnected and sustainable world.
Whether this tunnel becomes a reality or remains a dream beneath the waves, its mere proposal reminds us of humanity’s boundless ambition. It’s a vision that invites us to rethink what’s possible, daring us to push the boundaries of technology and imagination. The real question isn’t just if we can build it, but whether we’re ready to embrace the kind of global cooperation and bold innovation required to bring it to life.
News
We’re Going Back To The Moon! Meet The Crew Of Artemis II

For over half a century, the Moon has loomed in the night sky as both a symbol of human triumph and an unfulfilled promise. The Apollo missions left their footprints, but also unanswered questions—about what lies beyond, and what humanity’s next great leap might be. Now, with NASA’s Artemis program, we’re not just revisiting the Moon; we’re redefining our relationship with it.
Why go back? This time, it’s not just about planting flags or taking photographs. It’s about laying the foundation for humanity’s future in space. With Artemis II, a diverse team of astronauts is gearing up to embark on a journey that will push the boundaries of exploration and technology, paving the way for missions to Mars and beyond.

What Is Artemis II?
Artemis II represents the next pivotal step in humanity’s journey to explore deep space, serving as the first crewed mission in NASA’s Artemis program. Unlike the Apollo missions that preceded it, Artemis isn’t just about returning to the Moon—it’s about preparing for the future. This mission will orbit the Moon, testing critical systems and gathering essential data to ensure the safety and success of future lunar landings and even missions to Mars.
The spacecraft at the heart of Artemis II is the Orion capsule, powered by NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS), the most powerful rocket ever built. Together, they will carry the crew on a 10-day mission around the Moon, reaching a distance of over 230,000 miles from Earth. NASA officials describe it as “the next milestone in humanity’s quest to push farther into the solar system.”
According to NASA, Artemis II will provide an opportunity to “demonstrate key capabilities and operations needed for humans to live and work on another world.” It’s not just a technical test—it’s a statement of intent. As NASA Administrator Bill Nelson put it: “This is humanity’s next great chapter of exploration. Artemis II will help us chart a path to the Moon that is more inclusive, innovative, and ambitious than ever before.”
The Artemis program is also groundbreaking in its inclusivity, aiming to land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface. But before that can happen, Artemis II must ensure that everything is ready for Artemis III to safely achieve this historic milestone.
With technology that surpasses anything used during the Apollo missions and a clear vision for sustainable lunar exploration, Artemis II is setting the stage for a future where humanity can call the Moon more than just a distant neighbor—it could become a stepping stone to the stars.
Meet the Crew of Artemis II
At the heart of Artemis II lies its crew—four astronauts selected to represent the pinnacle of human achievement and the collaborative spirit of space exploration. Each of them brings a wealth of experience, skills, and a unique perspective to this historic mission.
Reid Wiseman (Commander)
Leading the mission is Reid Wiseman, a veteran astronaut with over 165 days in space during a previous expedition to the International Space Station (ISS). As Commander of Artemis II, Wiseman will oversee the mission’s operations, ensuring its success. Known for his leadership and dedication, Wiseman has said, “We are going to the Moon as one team, one crew, and one incredible global effort.”
Victor Glover (Pilot)
Making history as the first person of color to travel to the Moon, Victor Glover serves as the pilot of Artemis II. Glover previously spent 168 days aboard the ISS and contributed to multiple spacewalks. On his role in the mission, Glover remarked, “Representation matters. This mission is not just about where we’re going but who we’re taking along on this journey into the future.” His inclusion underscores NASA’s commitment to diversity and equity in space exploration.
Christina Koch (Mission Specialist)
Christina Koch is no stranger to breaking barriers. She holds the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman, spending 328 days in orbit during her time aboard the ISS. As a mission specialist, Koch will bring her expertise in engineering and space operations to Artemis II. “It is an honor to be part of a mission that paves the way for humanity’s next steps on the Moon and beyond,” Koch said about her historic selection.
Jeremy Hansen (Mission Specialist)
Representing the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), Jeremy Hansen becomes the first Canadian astronaut to venture beyond low Earth orbit. His inclusion highlights the international collaboration fueling the Artemis program. Hansen, a former fighter pilot, shared his excitement, saying, “I am humbled to represent Canada on this mission and to contribute to a global effort that will benefit all of humanity.”
Together, these four astronauts symbolize the ambition, courage, and diversity of the Artemis program. Their mission is not just to orbit the Moon but to inspire a generation to dream bigger and reach farther than ever before.

The Goals and Vision of Artemis II
Artemis II is more than a mission; it’s a defining moment in humanity’s effort to explore the unknown. With its primary goal of conducting a 10-day crewed lunar flyby, the mission serves as a crucial stepping stone for NASA’s long-term vision of sustainable exploration on the Moon and beyond. It’s the bridge between testing uncrewed systems in Artemis I and achieving a historic lunar landing in Artemis III.
The mission will focus on validating the life-support systems and performance of the Orion spacecraft in a deep-space environment. These tests are vital to ensuring the safety of future astronauts who will eventually live and work on the lunar surface. NASA describes Artemis II as “a mission designed to test every system, every capability, and every moment of human readiness needed for long-term exploration.”
Beyond the technical achievements, Artemis II has a broader purpose: advancing scientific discovery and inspiring a new generation of explorers. As part of its objectives, the Artemis program aims to establish a sustainable presence on the Moon by the end of the decade. This includes constructing the Lunar Gateway, a space station that will orbit the Moon and act as a hub for research and exploration.
According to NASA, these efforts are part of the agency’s commitment to using the Moon as a stepping stone for even greater ambitions, such as sending humans to Mars. “Artemis is not just a mission to the Moon; it’s humanity’s pathway to the stars,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
By combining cutting-edge technology with a bold vision for the future, Artemis II is laying the groundwork for a new era of exploration. It’s a mission that doesn’t just look to the Moon but far beyond—toward a future where humanity’s reach truly knows no bounds.
The Global Collaboration Driving Artemis II
Artemis II is a testament to the power of international collaboration, with space agencies from around the world joining forces to make this historic mission possible. While NASA leads the charge, the inclusion of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the European Space Agency (ESA) highlights how humanity’s reach into the cosmos is a shared endeavor.
One of the most symbolic aspects of this collaboration is the participation of Jeremy Hansen, the Canadian astronaut who will become the first non-American to venture beyond low Earth orbit. Canada’s contribution to Artemis includes the development of Canadarm3, an advanced robotic system that will be used on the Lunar Gateway. Hansen reflected on the significance of his role, saying, “This mission proves what we can achieve when we work together—nations united by curiosity, ambition, and a common goal.”
The European Space Agency has also played a pivotal role, supplying the European Service Module (ESM), which powers and propels the Orion spacecraft. The ESM provides air, water, and electricity for the astronauts, making it an indispensable part of the mission. “The European Service Module is at the heart of this mission,” ESA officials said, emphasizing its role as a foundation for future human exploration.
This spirit of global cooperation is central to the Artemis program’s vision of inclusivity and shared progress. NASA Administrator Bill Nelson stated, “The Artemis missions are not just about America going to the Moon; they’re about humanity going to the Moon. Together, we’re proving what’s possible.”
The international partnerships behind Artemis II not only strengthen diplomatic ties but also ensure that the mission benefits all of humanity. By pooling expertise, resources, and innovation, these collaborations are creating opportunities that extend beyond national boundaries—reminding us that space exploration is a global effort driven by a shared dream.

The Technology Powering Artemis II
Artemis II stands as a showcase of cutting-edge technology, blending decades of engineering advancements with new innovations designed to push the boundaries of human exploration. At the heart of the mission are the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System (SLS), two groundbreaking systems that make Artemis II possible.
The Orion spacecraft serves as the astronauts’ home for the duration of the mission. Designed to withstand the harsh environment of deep space, Orion is equipped with advanced life-support systems, radiation shielding, and navigation technologies. Its European-built Service Module (ESM) supplies propulsion, electricity, and vital resources such as water and oxygen. According to ESA, “The European Service Module is the powerhouse of Orion, enabling it to go farther than any human-rated spacecraft before.”
Complementing Orion is the Space Launch System (SLS), NASA’s most powerful rocket ever built. Towering at 322 feet, the SLS generates a staggering 8.8 million pounds of thrust, enough to propel the crew on their journey to the Moon. NASA officials describe it as “the backbone of the Artemis program, designed to take us deeper into space than ever before.” The rocket’s performance during Artemis I demonstrated its capability, clearing the way for its crewed debut in Artemis II.
Another key innovation supporting Artemis II is the Launch Abort System (LAS), which ensures the astronauts’ safety in the event of an emergency during launch. This system, mounted atop the Orion spacecraft, can pull the crew to safety within milliseconds, showcasing the program’s commitment to prioritizing human life.
Together, these technologies represent the pinnacle of human ingenuity. They are not only enabling the Artemis II mission but are also laying the foundation for future lunar landings and interplanetary travel. As NASA’s Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy stated, “Artemis II is proof that we have the tools, the talent, and the tenacity to explore beyond our world.”
By integrating proven systems with innovative designs, Artemis II serves as a blueprint for the future of space exploration, showing what’s possible when ambition meets cutting-edge technology.
-

 Awareness5 days ago
Awareness5 days agoMarathon runner diagnosed with terminal cancer urges people not to dismiss small symptom he experienced
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week ago9 Eerie Stories Of Third Man Syndrome, When People Claimed An Unseen Presence Helped Them Survive A Disaster
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoJames Franco Explained How Life Is Now Different After Being ‘Cast Out’ of Hollywood
-

 Awareness2 weeks ago
Awareness2 weeks ago‘Bleeding Eye’ Virus Sparks Travel Warning and Worldwide Concern – What Is the Incurable Disease?






